Updating Related Data with the Entity Framework in an ASP.NET MVC Application
by Tom Dykstra
Download Completed Project or Download PDF
The Contoso University sample web application demonstrates how to create ASP.NET MVC 5 applications using the Entity Framework 6 Code First and Visual Studio 2013. For information about the tutorial series, see the first tutorial in the series.
In the previous tutorial you displayed related data; in this tutorial you’ll update related data. For most relationships, this can be done by updating either foreign key fields or navigation properties. For many-to-many relationships, the Entity Framework doesn’t expose the join table directly, so you add and remove entities to and from the appropriate navigation properties.
The following illustrations show some of the pages that you’ll work with.
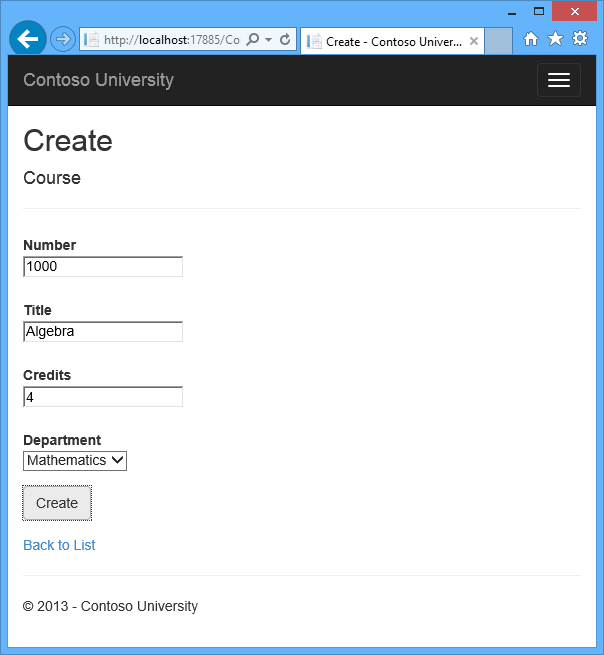
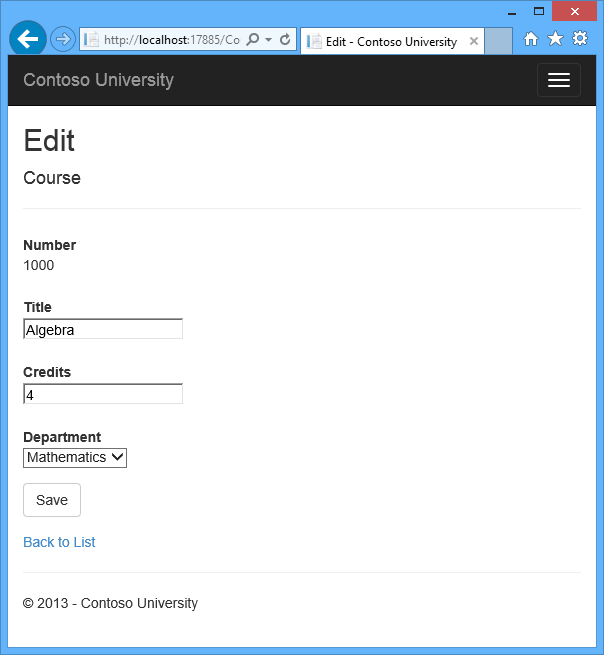
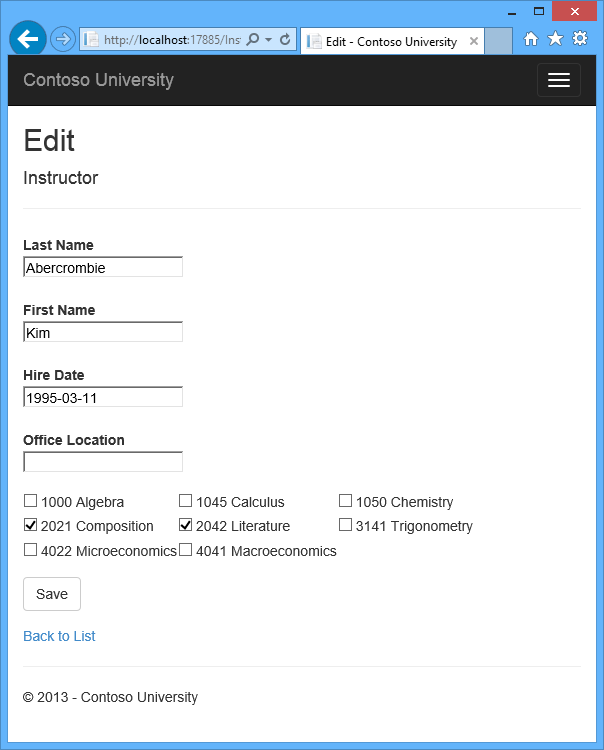
Customize the Create and Edit Pages for Courses
When a new course entity is created, it must have a relationship to an existing department. To facilitate this, the scaffolded code includes controller methods and Create and Edit views that include a drop-down list for selecting the department. The drop-down list sets the Course.DepartmentID foreign key property, and that’s all the Entity Framework needs in order to load the Department navigation property with the appropriate Department entity. You’ll use the scaffolded code, but change it slightly to add error handling and sort the drop-down list.
In CourseController.cs, delete the four Create and Edit methods and replace them with the following code:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Create()
2: {
3: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList();
4: return View();
5: }
6:
7: [HttpPost]
8: [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
9: public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include = "CourseID,Title,Credits,DepartmentID")]Course course)
10: {
11: try
12: {
13: if (ModelState.IsValid)
14: {
15: db.Courses.Add(course);
16: db.SaveChanges();
17: return RedirectToAction("Index");
18: }
19: }
20: catch (RetryLimitExceededException /* dex */)
21: {
22: //Log the error (uncomment dex variable name and add a line here to write a log.)
23: ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator.");
24: }
25: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID);
26: return View(course);
27: }
28:
29: public ActionResult Edit(int? id)
30: {
31: if (id == null)
32: {
33: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
34: }
35: Course course = db.Courses.Find(id);
36: if (course == null)
37: {
38: return HttpNotFound();
39: }
40: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID);
41: return View(course);
42: }
43:
44: [HttpPost, ActionName("Edit")]
45: [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
46: public ActionResult EditPost(int? id)
47: {
48: if (id == null)
49: {
50: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
51: }
52: var courseToUpdate = db.Courses.Find(id);
53: if (TryUpdateModel(courseToUpdate, "",
54: new string[] { "Title", "Credits", "DepartmentID" }))
55: {
56: try
57: {
58: db.SaveChanges();
59:
60: return RedirectToAction("Index");
61: }
62: catch (RetryLimitExceededException /* dex */)
63: {
64: //Log the error (uncomment dex variable name and add a line here to write a log.
65: ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator.");
66: }
67: }
68: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(courseToUpdate.DepartmentID);
69: return View(courseToUpdate);
70: }
71:
72: private void PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(object selectedDepartment = null)
73: {
74: var departmentsQuery = from d in db.Departments
75: orderby d.Name
76: select d;
77: ViewBag.DepartmentID = new SelectList(departmentsQuery, "DepartmentID", "Name", selectedDepartment);
78: }
Add the following using statement at the beginning of the file:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
The PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList method gets a list of all departments sorted by name, creates a SelectList collection for a drop-down list, and passes the collection to the view in a ViewBag property. The method accepts the optional selectedDepartment parameter that allows the calling code to specify the item that will be selected when the drop-down list is rendered. The view will pass the name DepartmentID to the DropDownList helper, and the helper then knows to look in the ViewBag object for a SelectList named DepartmentID.
The HttpGet Create method calls the PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList method without setting the selected item, because for a new course the department is not established yet:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Create()
2: {
3: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList();
4: return View();
5: }
The HttpGet Edit method sets the selected item, based on the ID of the department that is already assigned to the course being edited:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Edit(int? id)
2: {
3: if (id == null)
4: {
5: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
6: }
7: Course course = db.Courses.Find(id);
8: if (course == null)
9: {
10: return HttpNotFound();
11: }
12: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID);
13: return View(course);
14: }
The HttpPost methods for both Create and Edit also include code that sets the selected item when they redisplay the page after an error:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: catch (RetryLimitExceededException /* dex */)
2: {
3: //Log the error (uncomment dex variable name and add a line here to write a log.)
4: ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator.");
5: }
6: PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID);
7: return View(course);
This code ensures that when the page is redisplayed to show the error message, whatever department was selected stays selected.
The Course views are already scaffolded with drop-down lists for the department field, but you don’t want the DepartmentID caption for this field, so make the following highlighted change to the Views.cshtml file to change the caption.
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: @model ContosoUniversity.Models.Course
2:
3: @{
4: ViewBag.Title = "Create";
5: }
6:
7: <h2>Create</h2>
8:
9: @using (Html.BeginForm())
10: {
11: @Html.AntiForgeryToken()
12:
13: <div class="form-horizontal">
14: <h4>Course</h4>
15: <hr />
16: @Html.ValidationSummary(true)
17:
18: <div class="form-group">
19: @Html.LabelFor(model => model.CourseID, new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
20: <div class="col-md-10">
21: @Html.EditorFor(model => model.CourseID)
22: @Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.CourseID)
23: </div>
24: </div>
25:
26: <div class="form-group">
27: @Html.LabelFor(model => model.Title, new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
28: <div class="col-md-10">
29: @Html.EditorFor(model => model.Title)
30: @Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Title)
31: </div>
32: </div>
33:
34: <div class="form-group">
35: @Html.LabelFor(model => model.Credits, new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
36: <div class="col-md-10">
37: @Html.EditorFor(model => model.Credits)
38: @Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Credits)
39: </div>
40: </div>
41:
42: <div class="form-group">
43: <label class="control-label col-md-2" for="DepartmentID">Department</label>
44: <div class="col-md-10">
45: @Html.DropDownList("DepartmentID", String.Empty)
46: @Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.DepartmentID)
47: </div>
48: </div>
49:
50: <div class="form-group">
51: <div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
52: <input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-default" />
53: </div>
54: </div>
55: </div>
56: }
57:
58: <div>
59: @Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
60: </div>
61:
62: @section Scripts {
63: @Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
64: }
Make the same change in Views.cshtml.
Normally the scaffolder doesn’t scaffold a primary key because the key value is generated by the database and can’t be changed and isn’t a meaningful value to be displayed to users. For Course entities the scaffolder does include an text box for the CourseID field because it understands that the DatabaseGeneratedOption.None attribute means the user should be able enter the primary key value. But it doesn’t understand that because the number is meaningful you want to see it in the other views, so you need to add it manually.
In Views.cshtml, add a course number field before the Title field. Because it’s the primary key, it’s displayed, but it can’t be changed.
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <div class="form-group">
2: @Html.LabelFor(model => model.CourseID, new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
3: <div class="col-md-10">
4: @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.CourseID)
5: </div>
6: </div>
There’s already a hidden field (Html.HiddenFor helper) for the course number in the Edit view. Adding an Html.LabelFor helper doesn’t eliminate the need for the hidden field because it doesn’t cause the course number to be included in the posted data when the user clicks Save on the Edit page.
In Views.cshtml and Views.cshtml, change the department name caption from “Name” to “Department” and add a course number field before the Title field.
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <dt>
2: Department
3: </dt>
4:
5: <dd>
6: @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Department.Name)
7: </dd>
8:
9: <dt>
10: @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.CourseID)
11: </dt>
12:
13: <dd>
14: @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.CourseID)
15: </dd>
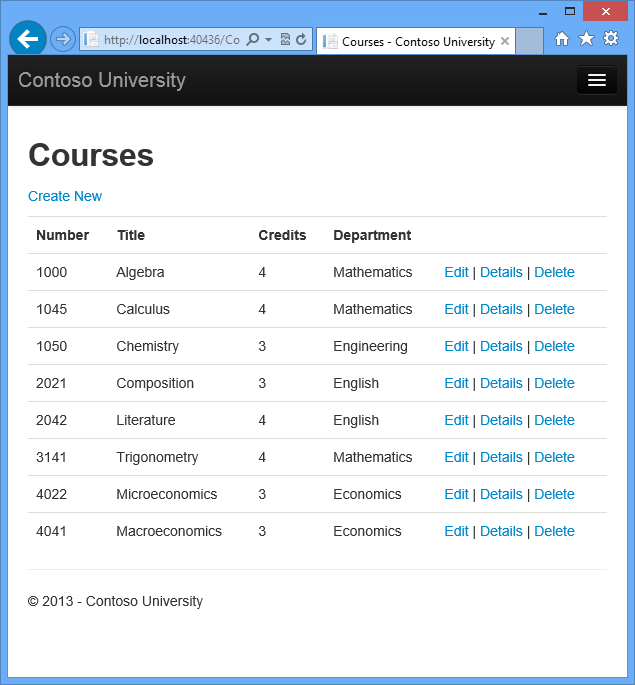
Run the Create page (display the Course Index page and click Create New) and enter data for a new course:
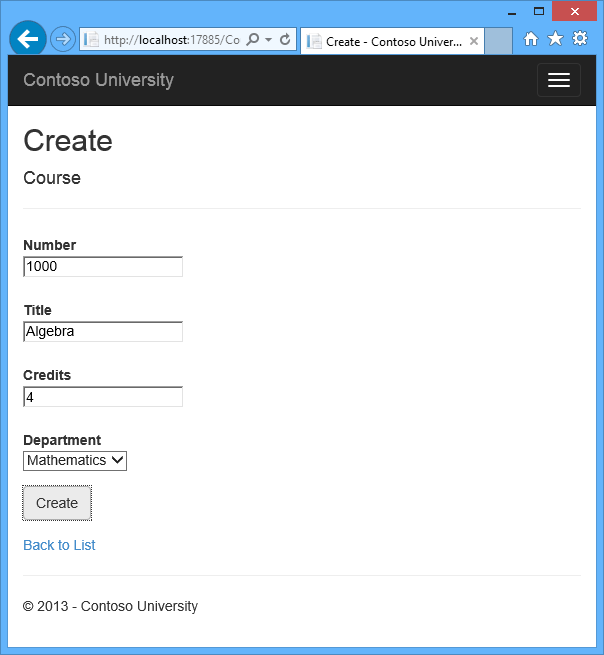
Click Create. The Course Index page is displayed with the new course added to the list. The department name in the Index page list comes from the navigation property, showing that the relationship was established correctly.
Run the Edit page (display the Course Index page and click Edit on a course).
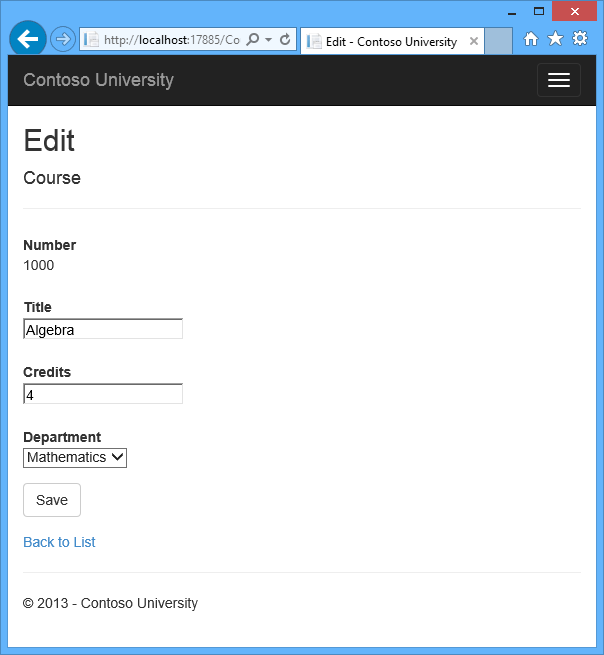
Change data on the page and click Save. The Course Index page is displayed with the updated course data.
Adding an Edit Page for Instructors
When you edit an instructor record, you want to be able to update the instructor’s office assignment. The Instructor entity has a one-to-zero-or-one relationship with the OfficeAssignment entity, which means you must handle the following situations:
- If the user clears the office assignment and it originally had a value, you must remove and delete the
OfficeAssignmententity. - If the user enters an office assignment value and it originally was empty, you must create a new
OfficeAssignmententity. - If the user changes the value of an office assignment, you must change the value in an existing
OfficeAssignmententity.
Open InstructorController.cs and look at the HttpGet Edit method:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: {
2: if (id == null)
3: {
4: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
5: }
6: Instructor instructor = db.Instructors.Find(id);
7: if (instructor == null)
8: {
9: return HttpNotFound();
10: }
11: ViewBag.ID = new SelectList(db.OfficeAssignments, "InstructorID", "Location", instructor.ID);
12: return View(instructor);
13: }
The scaffolded code here isn’t what you want. It’s setting up data for a drop-down list, but you what you need is a text box. Replace this method with the following code:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Edit(int? id)
2: {
3: if (id == null)
4: {
5: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
6: }
7: Instructor instructor = db.Instructors
8: .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
9: .Where(i => i.ID == id)
10: .Single();
11: if (instructor == null)
12: {
13: return HttpNotFound();
14: }
15: return View(instructor);
16: }
This code drops the ViewBag statement and adds eager loading for the associated OfficeAssignment entity. You can’t perform eager loading with the Find method, so the Where and Single methods are used instead to select the instructor.
Replace the HttpPost Edit method with the following code. which handles office assignment updates:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: [HttpPost, ActionName("Edit")]
2: [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
3: public ActionResult EditPost(int? id)
4: {
5: if (id == null)
6: {
7: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
8: }
9: var instructorToUpdate = db.Instructors
10: .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
11: .Where(i => i.ID == id)
12: .Single();
13:
14: if (TryUpdateModel(instructorToUpdate, "",
15: new string[] { "LastName", "FirstMidName", "HireDate", "OfficeAssignment" }))
16: {
17: try
18: {
19: if (String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(instructorToUpdate.OfficeAssignment.Location))
20: {
21: instructorToUpdate.OfficeAssignment = null;
22: }
23:
24: db.SaveChanges();
25:
26: return RedirectToAction("Index");
27: }
28: catch (RetryLimitExceededException /* dex */)
29: {
30: //Log the error (uncomment dex variable name and add a line here to write a log.
31: ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator.");
32: }
33: }
34: return View(instructorToUpdate);
35: }
The reference to RetryLimitExceededException requires a using statement; to add it, right-click RetryLimitExceededException, and then click Resolve - using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.

The code does the following:
- Changes the method name to
EditPostbecause the signature is now the same as theHttpGetmethod (theActionNameattribute specifies that the /Edit/ URL is still used). - Gets the current
Instructorentity from the database using eager loading for theOfficeAssignmentnavigation property. This is the same as what you did in theHttpGetEditmethod. Updates the retrieved
[!code-csharpMain]Instructorentity with values from the model binder. The TryUpdateModel overload used enables you to whitelist the properties you want to include. This prevents over-posting, as explained in the second tutorial.1: if (TryUpdateModel(instructorToUpdate, "",
2: new string[] { "LastName", "FirstMidName", "HireDate", "OfficeAssignment" }))
If the office location is blank, sets the
[!code-csharpMain]Instructor.OfficeAssignmentproperty to null so that the related row in theOfficeAssignmenttable will be deleted.1: if (String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(instructorToUpdate.OfficeAssignment.Location))
2: {3: instructorToUpdate.OfficeAssignment = null;
4: }Saves the changes to the database.
In Views.cshtml, after the div elements for the Hire Date field, add a new field for editing the office location:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <div class="form-group">
2: @Html.LabelFor(model => model.OfficeAssignment.Location, new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
3: <div class="col-md-10">
4: @Html.EditorFor(model => model.OfficeAssignment.Location)
5: @Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.OfficeAssignment.Location)
6: </div>
7: </div>
Run the page (select the Instructors tab and then click Edit on an instructor). Change the Office Location and click Save.

Adding Course Assignments to the Instructor Edit Page
Instructors may teach any number of courses. Now you’ll enhance the Instructor Edit page by adding the ability to change course assignments using a group of check boxes, as shown in the following screen shot:

The relationship between the Course and Instructor entities is many-to-many, which means you do not have direct access to the foreign key properties which are in the join table. Instead, you add and remove entities to and from the Instructor.Courses navigation property.
The UI that enables you to change which courses an instructor is assigned to is a group of check boxes. A check box for every course in the database is displayed, and the ones that the instructor is currently assigned to are selected. The user can select or clear check boxes to change course assignments. If the number of courses were much greater, you would probably want to use a different method of presenting the data in the view, but you’d use the same method of manipulating navigation properties in order to create or delete relationships.
To provide data to the view for the list of check boxes, you’ll use a view model class. Create AssignedCourseData.cs in the ViewModels folder and replace the existing code with the following code:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: namespace ContosoUniversity.ViewModels
2: {
3: public class AssignedCourseData
4: {
5: public int CourseID { get; set; }
6: public string Title { get; set; }
7: public bool Assigned { get; set; }
8: }
9: }
In InstructorController.cs, replace the HttpGet Edit method with the following code. The changes are highlighted.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Edit(int? id)
2: {
3: if (id == null)
4: {
5: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
6: }
7: Instructor instructor = db.Instructors
8: .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
9: .Include(i => i.Courses)
10: .Where(i => i.ID == id)
11: .Single();
12: PopulateAssignedCourseData(instructor);
13: if (instructor == null)
14: {
15: return HttpNotFound();
16: }
17: return View(instructor);
18: }
19:
20: private void PopulateAssignedCourseData(Instructor instructor)
21: {
22: var allCourses = db.Courses;
23: var instructorCourses = new HashSet<int>(instructor.Courses.Select(c => c.CourseID));
24: var viewModel = new List<AssignedCourseData>();
25: foreach (var course in allCourses)
26: {
27: viewModel.Add(new AssignedCourseData
28: {
29: CourseID = course.CourseID,
30: Title = course.Title,
31: Assigned = instructorCourses.Contains(course.CourseID)
32: });
33: }
34: ViewBag.Courses = viewModel;
35: }
The code adds eager loading for the Courses navigation property and calls the new PopulateAssignedCourseData method to provide information for the check box array using the AssignedCourseData view model class.
The code in the PopulateAssignedCourseData method reads through all Course entities in order to load a list of courses using the view model class. For each course, the code checks whether the course exists in the instructor’s Courses navigation property. To create efficient lookup when checking whether a course is assigned to the instructor, the courses assigned to the instructor are put into a HashSet collection. The Assigned property is set to true for courses the instructor is assigned. The view will use this property to determine which check boxes must be displayed as selected. Finally, the list is passed to the view in a ViewBag property.
Next, add the code that’s executed when the user clicks Save. Replace the EditPost method with the following code, which calls a new method that updates the Courses navigation property of the Instructor entity. The changes are highlighted.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: [HttpPost]
2: [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
3: public ActionResult Edit(int? id, string[] selectedCourses)
4: {
5: if (id == null)
6: {
7: return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
8: }
9: var instructorToUpdate = db.Instructors
10: .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
11: .Include(i => i.Courses)
12: .Where(i => i.ID == id)
13: .Single();
14:
15: if (TryUpdateModel(instructorToUpdate, "",
16: new string[] { "LastName", "FirstMidName", "HireDate", "OfficeAssignment" }))
17: {
18: try
19: {
20: if (String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(instructorToUpdate.OfficeAssignment.Location))
21: {
22: instructorToUpdate.OfficeAssignment = null;
23: }
24:
25: UpdateInstructorCourses(selectedCourses, instructorToUpdate);
26:
27: db.SaveChanges();
28:
29: return RedirectToAction("Index");
30: }
31: catch (RetryLimitExceededException /* dex */)
32: {
33: //Log the error (uncomment dex variable name and add a line here to write a log.
34: ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator.");
35: }
36: }
37: PopulateAssignedCourseData(instructorToUpdate);
38: return View(instructorToUpdate);
39: }
40: private void UpdateInstructorCourses(string[] selectedCourses, Instructor instructorToUpdate)
41: {
42: if (selectedCourses == null)
43: {
44: instructorToUpdate.Courses = new List<Course>();
45: return;
46: }
47:
48: var selectedCoursesHS = new HashSet<string>(selectedCourses);
49: var instructorCourses = new HashSet<int>
50: (instructorToUpdate.Courses.Select(c => c.CourseID));
51: foreach (var course in db.Courses)
52: {
53: if (selectedCoursesHS.Contains(course.CourseID.ToString()))
54: {
55: if (!instructorCourses.Contains(course.CourseID))
56: {
57: instructorToUpdate.Courses.Add(course);
58: }
59: }
60: else
61: {
62: if (instructorCourses.Contains(course.CourseID))
63: {
64: instructorToUpdate.Courses.Remove(course);
65: }
66: }
67: }
68: }
The method signature is now different from the HttpGet Edit method, so the method name changes from EditPost back to Edit.
Since the view doesn’t have a collection of Course entities, the model binder can’t automatically update the Courses navigation property. Instead of using the model binder to update the Courses navigation property, you’ll do that in the new UpdateInstructorCourses method. Therefore you need to exclude the Courses property from model binding. This doesn’t require any change to the code that calls TryUpdateModel because you’re using the whitelisting overload and Courses isn’t in the include list.
If no check boxes were selected, the code in UpdateInstructorCourses initializes the Courses navigation property with an empty collection:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: if (selectedCourses == null)
2: {
3: instructorToUpdate.Courses = new List<Course>();
4: return;
5: }
The code then loops through all courses in the database and checks each course against the ones currently assigned to the instructor versus the ones that were selected in the view. To facilitate efficient lookups, the latter two collections are stored in HashSet objects.
If the check box for a course was selected but the course isn’t in the Instructor.Courses navigation property, the course is added to the collection in the navigation property.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: if (selectedCoursesHS.Contains(course.CourseID.ToString()))
2: {
3: if (!instructorCourses.Contains(course.CourseID))
4: {
5: instructorToUpdate.Courses.Add(course);
6: }
7: }
If the check box for a course wasn’t selected, but the course is in the Instructor.Courses navigation property, the course is removed from the navigation property.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: else
2: {
3: if (instructorCourses.Contains(course.CourseID))
4: {
5: instructorToUpdate.Courses.Remove(course);
6: }
7: }
In Views.cshtml, add a Courses field with an array of check boxes by adding the following code immediately after the div elements for the OfficeAssignment field and before the div element for the Save button:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <div class="form-group">
2: <div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
3: <table>
4: <tr>
5: @{
6: int cnt = 0;
7: List<ContosoUniversity.ViewModels.AssignedCourseData> courses = ViewBag.Courses;
8:
9: foreach (var course in courses)
10: {
11: if (cnt++ % 3 == 0)
12: {
13: @:</tr><tr>
14: }
15: @:<td>
16: <input type="checkbox"
17: name="selectedCourses"
18: value="@course.CourseID"
19: @(Html.Raw(course.Assigned ? "checked=\"checked\"" : "")) />
20: @course.CourseID @: @course.Title
21: @:</td>
22: }
23: @:</tr>
24: }
25: </table>
26: </div>
27: </div>
After you paste the code, if line breaks and indentation don’t look like they do here, manually fix everything so that it looks like what you see here. The indentation doesn’t have to be perfect, but the @</tr><tr>, @:<td>, @:</td>, and @</tr> lines must each be on a single line as shown or you’ll get a runtime error.
This code creates an HTML table that has three columns. In each column is a check box followed by a caption that consists of the course number and title. The check boxes all have the same name (“selectedCourses”), which informs the model binder that they are to be treated as a group. The value attribute of each check box is set to the value of CourseID. When the page is posted, the model binder passes an array to the controller that consists of the CourseID values for only the check boxes which are selected.
When the check boxes are initially rendered, those that are for courses assigned to the instructor have checked attributes, which selects them (displays them checked).
After changing course assignments, you’ll want to be able to verify the changes when the site returns to the Index page. Therefore, you need to add a column to the table in that page. In this case you don’t need to use the ViewBag object, because the information you want to display is already in the Courses navigation property of the Instructor entity that you’re passing to the page as the model.
In Views.cshtml, add a Courses heading immediately following the Office heading, as shown in the following example:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <tr>
2: <th>Last Name</th>
3: <th>First Name</th>
4: <th>Hire Date</th>
5: <th>Office</th>
6: <th>Courses</th>
7: <th></th>
8: </tr>
Then add a new detail cell immediately following the office location detail cell:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <td>
2: @if (item.OfficeAssignment != null)
3: {
4: @item.OfficeAssignment.Location
5: }
6: </td>
7: <td>
8: @{
9: foreach (var course in item.Courses)
10: {
11: @course.CourseID @: @course.Title <br />
12: }
13: }
14: </td>
15: <td>
16: @Html.ActionLink("Select", "Index", new { id = item.ID }) |
17: @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id = item.ID }) |
18: @Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id = item.ID }) |
19: @Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id = item.ID })
20: </td>
Run the Instructor Index page to see the courses assigned to each instructor:
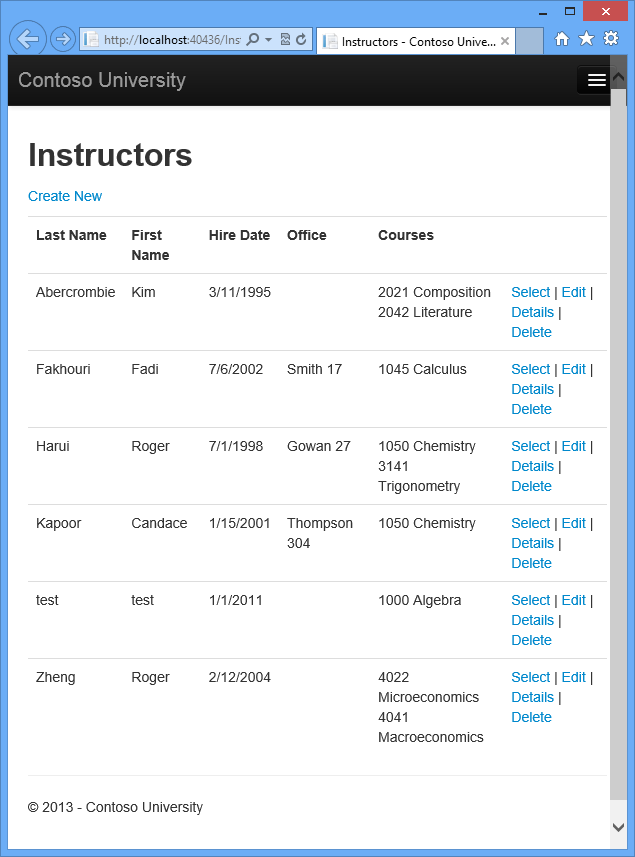
Click Edit on an instructor to see the Edit page.
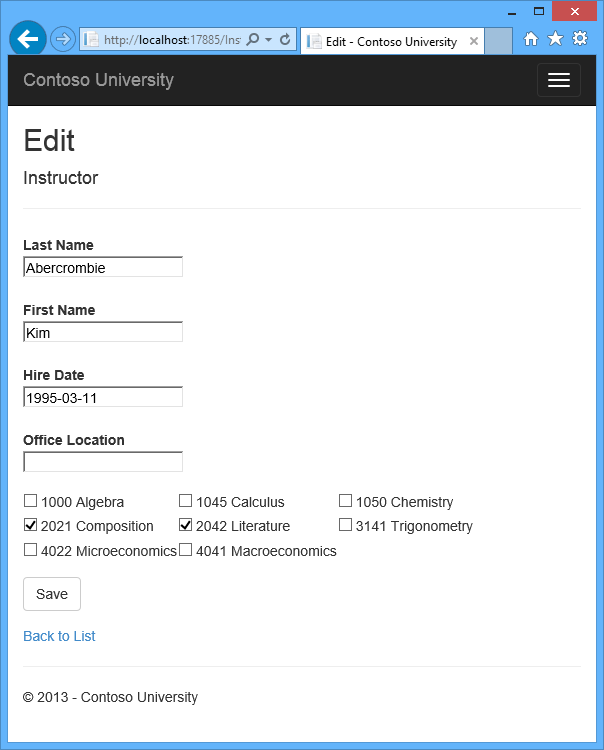
Change some course assignments and click Save. The changes you make are reflected on the Index page.
Note: The approach taken here to edit instructor course data works well when there is a limited number of courses. For collections that are much larger, a different UI and a different updating method would be required.
Update the DeleteConfirmed Method
In InstructorController.cs, delete the DeleteConfirmed method and insert the following code in its place.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: [HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
2: [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
3: public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
4: {
5: Instructor instructor = db.Instructors
6: .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
7: .Where(i => i.ID == id)
8: .Single();
9:
10: db.Instructors.Remove(instructor);
11:
12: var department = db.Departments
13: .Where(d => d.InstructorID == id)
14: .SingleOrDefault();
15: if (department != null)
16: {
17: department.InstructorID = null;
18: }
19:
20: db.SaveChanges();
21: return RedirectToAction("Index");
22: }
This code makes the following change:
- If the instructor is assigned as administrator of any department, removes the instructor assignment from that department. Without this code, you would get a referential integrity error if you tried to delete an instructor who was assigned as administrator for a department.
This code doesn’t handle the scenario of one instructor assigned as administrator for multiple departments. In the last tutorial you’ll add code that prevents that scenario from happening.
Add office location and courses to the Create page
In InstructorController.cs, delete the HttpGet and HttpPost Create methods, and then add the following code in their place:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Create()
2: {
3: var instructor = new Instructor();
4: instructor.Courses = new List<Course>();
5: PopulateAssignedCourseData(instructor);
6: return View();
7: }
8:
9: [HttpPost]
10: [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
11: public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include = "LastName,FirstMidName,HireDate,OfficeAssignment" )]Instructor instructor, string[] selectedCourses)
12: {
13: if (selectedCourses != null)
14: {
15: instructor.Courses = new List<Course>();
16: foreach (var course in selectedCourses)
17: {
18: var courseToAdd = db.Courses.Find(int.Parse(course));
19: instructor.Courses.Add(courseToAdd);
20: }
21: }
22: if (ModelState.IsValid)
23: {
24: db.Instructors.Add(instructor);
25: db.SaveChanges();
26: return RedirectToAction("Index");
27: }
28: PopulateAssignedCourseData(instructor);
29: return View(instructor);
30: }
This code is similar to what you saw for the Edit methods except that initially no courses are selected. The HttpGet Create method calls the PopulateAssignedCourseData method not because there might be courses selected but in order to provide an empty collection for the foreach loop in the view (otherwise the view code would throw a null reference exception).
The HttpPost Create method adds each selected course to the Courses navigation property before the template code that checks for validation errors and adds the new instructor to the database. Courses are added even if there are model errors so that when there are model errors (for an example, the user keyed an invalid date) so that when the page is redisplayed with an error message, any course selections that were made are automatically restored.
Notice that in order to be able to add courses to the Courses navigation property you have to initialize the property as an empty collection:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: instructor.Courses = new List<Course>();
As an alternative to doing this in controller code, you could do it in the Instructor model by changing the property getter to automatically create the collection if it doesn’t exist, as shown in the following example:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: private ICollection<Course> _courses;
2: public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses
3: {
4: get
5: {
6: return _courses ?? (_courses = new List<Course>());
7: }
8: set
9: {
10: _courses = value;
11: }
12: }
If you modify the Courses property in this way, you can remove the explicit property initialization code in the controller.
In Views.cshtml, add an office location text box and course check boxes after the hire date field and before the Submit button.
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: <div class="form-group">
2: @Html.LabelFor(model => model.OfficeAssignment.Location, new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
3: <div class="col-md-10">
4: @Html.EditorFor(model => model.OfficeAssignment.Location)
5: @Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.OfficeAssignment.Location)
6: </div>
7: </div>
8:
9: <div class="form-group">
10: <div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
11: <table>
12: <tr>
13: @{
14: int cnt = 0;
15: List<ContosoUniversity.ViewModels.AssignedCourseData> courses = ViewBag.Courses;
16:
17: foreach (var course in courses)
18: {
19: if (cnt++ % 3 == 0)
20: {
21: @:</tr><tr>
22: }
23: @:<td>
24: <input type="checkbox"
25: name="selectedCourses"
26: value="@course.CourseID"
27: @(Html.Raw(course.Assigned ? "checked=\"checked\"" : "")) />
28: @course.CourseID @: @course.Title
29: @:</td>
30: }
31: @:</tr>
32: }
33: </table>
34: </div>
35: </div>
After you paste the code, fix line breaks and indentation as you did earlier for the Edit page.
Run the Create page and add an instructor.
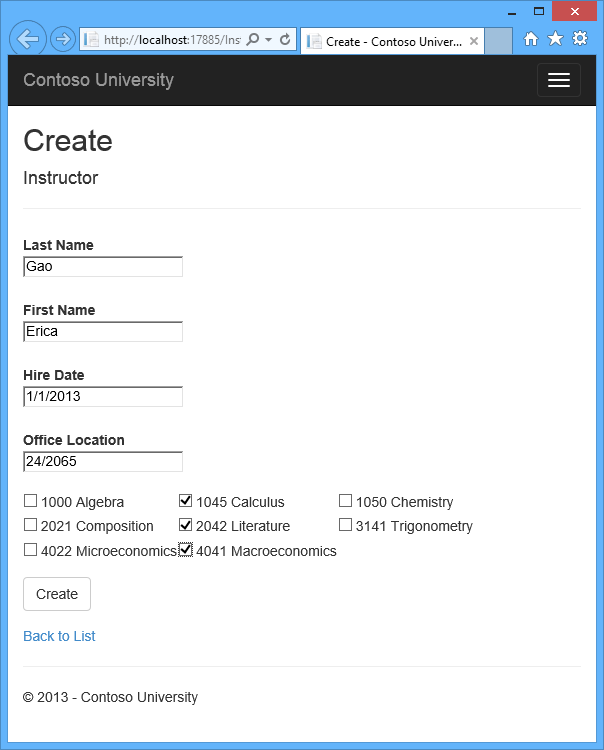
As explained in the Basic CRUD Functionality tutorial, by default the Entity Framework implicitly implements transactions. For scenarios where you need more control – for example, if you want to include operations done outside of Entity Framework in a transaction – see Working with Transactions on MSDN.
Summary
You have now completed this introduction to working with related data. So far in these tutorials you’ve worked with code that does synchronous I/O. You can make the application use web server resources more efficiently by implementing asynchronous code, and that’s what you’ll do in the next tutorial.
Please leave feedback on how you liked this tutorial and what we could improve. You can also request new topics at Show Me How With Code.
Links to other Entity Framework resources can be found in ASP.NET Data Access - Recommended Resources.
 )
)
|
|