Creating a Customized Sorting User Interface (VB)
Download Sample App or Download PDF
When displaying a long list of sorted data, it can be very helpful to group related data by introducing separator rows. In this tutorial we’ll see how to create such a sorting user interface.
Introduction
When displaying a long list of sorted data where there are only a handful of different values in the sorted column, an end user might find it hard to discern where, exactly, the difference boundaries occur. For example, there are 81 products in the database, but only nine different category choices (eight unique categories plus the NULL option). Consider the case of a user who is interested in examining the products that fall under the Seafood category. From a page that lists all of the products in a single GridView, the user might decide her best bet is to sort the results by category, which will group together all of the Seafood products together. After sorting by category, the user then needs to hunt through the list, looking for where the Seafood-grouped products start and end. Since the results are ordered alphabetically by the category name finding the Seafood products is not difficult, but it still requires closely scanning the list of items in the grid.
To help highlight the boundaries between sorted groups, many websites employ a user interface that adds a separator between such groups. Separators like the ones shown in Figure 1 enables a user to more quickly find a particular group and identify its boundaries, as well as ascertain what distinct groups exist in the data.
Figure 1: Each Category Group is Clearly Identified (Click to view full-size image)
In this tutorial we’ll see how to create such a sorting user interface.
Step 1: Creating a Standard, Sortable GridView
Before we explore how to augment the GridView to provide the enhanced sorting interface, let s first create a standard, sortable GridView that lists the products. Start by opening the CustomSortingUI.aspx page in the PagingAndSorting folder. Add a GridView to the page, set its ID property to ProductList, and bind it to a new ObjectDataSource. Configure the ObjectDataSource to use the ProductsBLL class s GetProducts() method for selecting records.
Next, configure the GridView such that it only contains the ProductName, CategoryName, SupplierName, and UnitPrice BoundFields and the Discontinued CheckBoxField. Finally, configure the GridView to support sorting by checking the Enable Sorting checkbox in the GridView s smart tag (or by setting its AllowSorting property to true). After making these additions to the CustomSortingUI.aspx page, the declarative markup should look similar to the following:
[!code-aspxMain]
1: <asp:GridView ID="ProductList" runat="server" AllowSorting="True"
2: AutoGenerateColumns="False" DataKeyNames="ProductID"
3: DataSourceID="ObjectDataSource1" EnableViewState="False">
4: <Columns>
5: <asp:BoundField DataField="ProductName" HeaderText="Product"
6: SortExpression="ProductName" />
7: <asp:BoundField DataField="CategoryName" HeaderText="Category"
8: ReadOnly="True" SortExpression="CategoryName" />
9: <asp:BoundField DataField="SupplierName" HeaderText="Supplier"
10: ReadOnly="True" SortExpression="SupplierName" />
11: <asp:BoundField DataField="UnitPrice" DataFormatString="{0:C}"
12: HeaderText="Price" HtmlEncode="False" SortExpression="UnitPrice" />
13: <asp:CheckBoxField DataField="Discontinued" HeaderText="Discontinued"
14: SortExpression="Discontinued" />
15: </Columns>
16: </asp:GridView>
17: <asp:ObjectDataSource ID="ObjectDataSource1" runat="server"
18: OldValuesParameterFormatString="original_{0}" SelectMethod="GetProducts"
19: TypeName="ProductsBLL"></asp:ObjectDataSource>
Take a moment to view our progress thus far in a browser. Figure 2 shows the sortable GridView when its data is sorted by category in alphabetical order.
Figure 2: The Sortable GridView s Data is Ordered by Category (Click to view full-size image)
Step 2: Exploring Techniques for Adding the Separator Rows
With the generic, sortable GridView complete, all that remains is to be able to add the separator rows in the GridView before each unique sorted group. But how can such rows be injected into the GridView? Essentially, we need to iterate through the GridView s rows, determine where the differences occur between the values in the sorted column, and then add the appropriate separator row. When thinking about this problem, it seems natural that the solution lies somewhere in the GridView s RowDataBound event handler. As we discussed in the Custom Formatting Based Upon Data tutorial, this event handler is commonly used when applying row-level formatting based on the row s data. However, the RowDataBound event handler is not the solution here, as rows cannot be added to the GridView programmatically from this event handler. The GridView s Rows collection, in fact, is read-only.
To add additional rows to the GridView we have three choices:
- Add these metadata separator rows to the actual data that is bound to the GridView
- After the GridView has been bound to the data, add additional
TableRowinstances to the GridView s control collection - Create a custom server control that extends the GridView control and overrides those methods responsible for constructing the GridView s structure
Creating a custom server control would be the best approach if this functionality was needed on many web pages or across several websites. However, it would entail quite a bit of code and a thorough exploration into the depths of the GridView s internal workings. Therefore, we’ll not consider that option for this tutorial.
The other two options adding separator rows to the actual data being bound to the GridView and manipulating the GridView s control collection after its been bound - attack the problem differently and merit a discussion.
Adding Rows to the Data Bound to the GridView
When the GridView is bound to a data source, it creates a GridViewRow for each record returned by the data source. Therefore, we can inject the needed separator rows by adding separator records to the data source before binding it to the GridView. Figure 3 illustrates this concept.
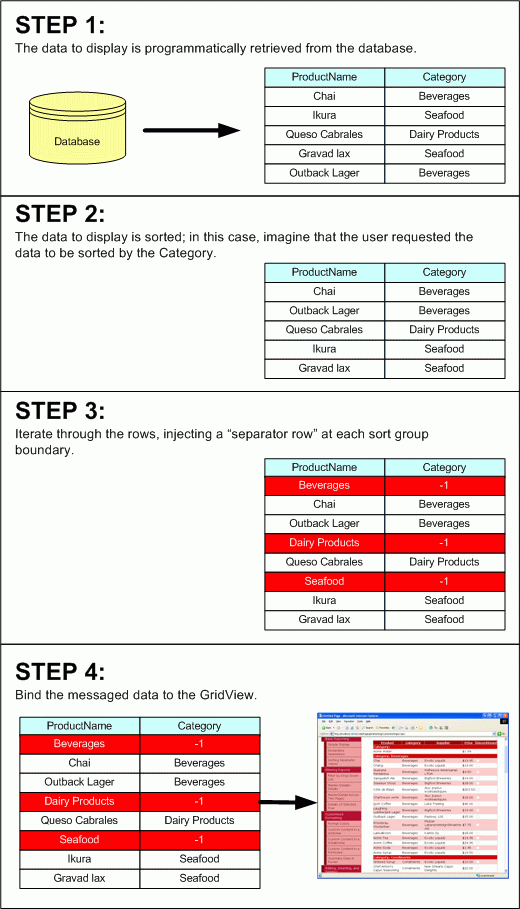
Figure 3: One Technique Involves Adding Separator Rows to the Data Source
I use the term separator records in quotes because there is no special separator record; rather, we must somehow flag that a particular record in the data source serves as a separator rather than a normal data row. For our examples, we re binding a ProductsDataTable instance to the GridView, which is composed of ProductRows. We might flag a record as a separator row by setting its CategoryID property to -1 (since such a value couldn t exist normally).
To utilize this technique we d need to perform the following steps:
- Programmatically retrieve the data to bind to the GridView (a
ProductsDataTableinstance) - Sort the data based on the GridView s
SortExpressionandSortDirectionproperties - Iterate through the
ProductsRowsin theProductsDataTable, looking for where the differences in the sorted column lie - At each group boundary, inject a separator record
ProductsRowinstance into the DataTable, one that has it sCategoryIDset to-1(or whatever designation was decided upon to mark a record as a separator record ) - After injecting the separator rows, programmatically bind the data to the GridView
In addition to these five steps, we d also need to provide an event handler for the GridView s RowDataBound event. Here, we d check each DataRow and determine if it was a separator row, one whose CategoryID setting was -1. If so, we d probably want to adjust its formatting or the text displayed in the cell(s).
Using this technique for injecting the sorting group boundaries requires a bit more work than outlined above, as you need to also provide an event handler for the GridView s Sorting event and keep track of the SortExpression and SortDirection values.
Manipulating the GridView s Control Collection After It s Been Databound
Rather than messaging the data before binding it to the GridView, we can add the separator rows after the data has been bound to the GridView. The process of data binding builds up the GridView s control hierarchy, which in reality is simply a Table instance composed of a collection of rows, each of which is composed of a collection of cells. Specifically, the GridView s control collection contains a Table object at its root, a GridViewRow (which is derived from the TableRow class) for each record in the DataSource bound to the GridView, and a TableCell object in each GridViewRow instance for each data field in the DataSource.
To add separator rows between each sorting group, we can directly manipulate this control hierarchy once it has been created. We can be confident that the GridView s control hierarchy has been created for the last time by the time the page is being rendered. Therefore, this approach overrides the Page class s Render method, at which point the GridView s final control hierarchy is updated to include the needed separator rows. Figure 4 illustrates this process.
Figure 4: An Alternate Technique Manipulates the GridView s Control Hierarchy (Click to view full-size image)
For this tutorial, we’ll use this latter approach to customize the sorting user experience.
[!NOTE] The code I m presenting in this tutorial is based on the example provided in Teemu Keiski s blog entry, Playing a Bit with GridView Sort Grouping.
Step 3: Adding the Separator Rows to the GridView s Control Hierarchy
Since we only want to add the separator rows to the GridView s control hierarchy after its control hierarchy has been created and created for the last time on that page visit, we want to perform this addition at the end of the page lifecycle, but before the actual GridView control hierarchy has been rendered into HTML. The latest possible point at which we can accomplish this is the Page class s Render event, which we can override in our code-behind class using the following method signature:
[!code-vbMain]
1: Protected Overrides Sub Render(ByVal writer As HtmlTextWriter)
2: ' Add code to manipulate the GridView control hierarchy
3: MyBase.Render(writer)
4: End Sub
When the Page class s original Render method is invoked base.Render(writer) each of the controls in the page will be rendered, generating the markup based on their control hierarchy. Therefore it is imperative that we both call base.Render(writer), so that the page is rendered, and that we manipulate the GridView s control hierarchy prior to calling base.Render(writer), so that the separator rows have been added to the GridView s control hierarchy before it s been rendered.
To inject the sort group headers we first need to ensure that the user has requested that the data be sorted. By default, the GridView s contents are not sorted, and therefore we don t need to enter any group sorting headers.
[!NOTE] If you want the GridView to be sorted by a particular column when the page is first loaded, call the GridView s
Sortmethod on the first page visit (but not on subsequent postbacks). To accomplish this, add this call in thePage_Loadevent handler within anif (!Page.IsPostBack)conditional. Refer back to the Paging and Sorting Report Data tutorial information for more on theSortmethod.
Assuming that the data has been sorted, our next task is to determine what column the data was sorted by and then to scan the rows looking for differences in that column s values. The following code ensures that the data has been sorted and finds the column by which the data has been sorted:
[!code-vbMain]
1: Protected Overrides Sub Render(ByVal writer As HtmlTextWriter)
2: ' Only add the sorting UI if the GridView is sorted
3: If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(ProductList.SortExpression) Then
4: ' Determine the index and HeaderText of the column that
5: 'the data is sorted by
6: Dim sortColumnIndex As Integer = -1
7: Dim sortColumnHeaderText As String = String.Empty
8: For i As Integer = 0 To ProductList.Columns.Count - 1
9: If ProductList.Columns(i).SortExpression.CompareTo( _
10: ProductList.SortExpression) = 0 Then
11: sortColumnIndex = i
12: sortColumnHeaderText = ProductList.Columns(i).HeaderText
13: Exit For
14: End If
15: Next
16: ' TODO: Scan the rows for differences in the sorted column�s values
17: End Sub
If the GridView has yet to be sorted, the GridView s SortExpression property will not have been set. Therefore, we only want to add the separator rows if this property has some value. If it does, we next need to determine the index of the column by which the data was sorted. This is accomplished by looping through the GridView s Columns collection, searching for the column whose SortExpression property equals the GridView s SortExpression property. In addition to the column s index, we also grab the HeaderText property, which is used when displaying the separator rows.
With the index of the column by which the data is sorted, the final step is to enumerate the rows of the GridView. For each row we need to determine whether the sorted column s value differs from the previous row s sorted column s value. If so, we need to inject a new GridViewRow instance into the control hierarchy. This is accomplished with the following code:
[!code-vbMain]
1: Protected Overrides Sub Render(ByVal writer As HtmlTextWriter)
2: ' Only add the sorting UI if the GridView is sorted
3: If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(ProductList.SortExpression) Then
4: ' ... Code for finding the sorted column index removed for brevity ...
5: ' Reference the Table the GridView has been rendered into
6: Dim gridTable As Table = CType(ProductList.Controls(0), Table)
7: ' Enumerate each TableRow, adding a sorting UI header if
8: ' the sorted value has changed
9: Dim lastValue As String = String.Empty
10: For Each gvr As GridViewRow In ProductList.Rows
11: Dim currentValue As String = gvr.Cells(sortColumnIndex).Text
12: If lastValue.CompareTo(currentValue) <> 0 Then
13: ' there's been a change in value in the sorted column
14: Dim rowIndex As Integer = gridTable.Rows.GetRowIndex(gvr)
15: ' Add a new sort header row
16: Dim sortRow As New GridViewRow(rowIndex, rowIndex, _
17: DataControlRowType.DataRow, DataControlRowState.Normal)
18: Dim sortCell As New TableCell()
19: sortCell.ColumnSpan = ProductList.Columns.Count
20: sortCell.Text = String.Format("{0}: {1}", _
21: sortColumnHeaderText, currentValue)
22: sortCell.CssClass = "SortHeaderRowStyle"
23: ' Add sortCell to sortRow, and sortRow to gridTable
24: sortRow.Cells.Add(sortCell)
25: gridTable.Controls.AddAt(rowIndex, sortRow)
26: ' Update lastValue
27: lastValue = currentValue
28: End If
29: Next
30: End If
31: MyBase.Render(writer)
32: End Sub
This code starts by programmatically referencing the Table object found at the root of the GridView s control hierarchy and creating a string variable named lastValue. lastValue is used to compare the current row s sorted column value with the previous row s value. Next, the GridView s Rows collection is enumerated and for each row the value of the sorted column is stored in the currentValue variable.
[!NOTE] To determine the value of the particular row s sorted column I use the cell s
Textproperty. This works well for BoundFields, but will not work as desired for TemplateFields, CheckBoxFields, and so on. We’ll look at how to account for alternate GridView fields shortly.
The currentValue and lastValue variables are then compared. If they differ we need to add a new separator row to the control hierarchy. This is accomplished by determining the index of the GridViewRow in the Table object s Rows collection, creating new GridViewRow and TableCell instances, and then adding the TableCell and GridViewRow to the control hierarchy.
Note that the separator row s lone TableCell is formatted such that it spans the entire width of the GridView, is formatted using the SortHeaderRowStyle CSS class, and has its Text property such that it shows both the sort group name (such as Category ) and the group s value (such as Beverages ). Finally, lastValue is updated to the value of currentValue.
The CSS class used to format the sorting group header row SortHeaderRowStyle needs to be specified in the Styles.css file. Feel free to use whatever style settings appeal to you; I used the following:
[!code-cssMain]
1: .SortHeaderRowStyle
2: {
3: background-color: #c00;
4: text-align: left;
5: font-weight: bold;
6: color: White;
7: }
With the current code, the sorting interface adds sort group headers when sorting by any BoundField (see Figure 5, which shows a screenshot when sorting by supplier). However, when sorting by any other field type (such as a CheckBoxField or TemplateField), the sort group headers are nowhere to be found (see Figure 6).
Figure 5: The Sorting Interface Includes Sort Group Headers When Sorting by BoundFields (Click to view full-size image)
Figure 6: The Sort Group Headers are Missing When Sorting a CheckBoxField (Click to view full-size image)
The reason the sort group headers are missing when sorting by a CheckBoxField is because the code currently uses just the TableCell s Text property to determine the value of the sorted column for each row. For CheckBoxFields, the TableCell s Text property is an empty string; instead, the value is available through a CheckBox Web control that resides within the TableCell s Controls collection.
To handle field types other than BoundFields, we need to augment the code where the currentValue variable is assigned to check for the existence of a CheckBox in the TableCell s Controls collection. Instead of using currentValue = gvr.Cells(sortColumnIndex).Text, replace this code with the following:
[!code-vbMain]
1: Dim currentValue As String = String.Empty
2: If gvr.Cells(sortColumnIndex).Controls.Count > 0 Then
3: If TypeOf gvr.Cells(sortColumnIndex).Controls(0) Is CheckBox Then
4: If CType(gvr.Cells(sortColumnIndex).Controls(0), CheckBox).Checked Then
5: currentValue = "Yes"
6: Else
7: currentValue = "No"
8: End If
9: ' ... Add other checks here if using columns with other
10: ' Web controls in them (Calendars, DropDownLists, etc.) ...
11: End If
12: Else
13: currentValue = gvr.Cells(sortColumnIndex).Text
14: End If
This code examines the sorted column TableCell for the current row to determine if there are any controls in the Controls collection. If there are, and the first control is a CheckBox, the currentValue variable is set to Yes or No, depending on the CheckBox s Checked property. Otherwise, the value is taken from the TableCell s Text property. This logic can be replicated to handle sorting for any TemplateFields that may exist in the GridView.
With the above code addition, the sort group headers are now present when sorting by the Discontinued CheckBoxField (see Figure 7).
Figure 7: The Sort Group Headers are Now Present When Sorting a CheckBoxField (Click to view full-size image)
[!NOTE] If you have products with
NULLdatabase values for theCategoryID,SupplierID, orUnitPricefields, those values will appear as empty strings in the GridView by default, meaning the separator row s text for those products withNULLvalues will read like Category: (that is, there s no name after Category: like with Category: Beverages ). If you want a value displayed here you can either set the BoundFieldsNullDisplayTextproperty to the text you want displayed or you can add a conditional statement in the Render method when assigning thecurrentValueto the separator row sTextproperty.
Summary
The GridView does not include many built-in options for customizing the sorting interface. However, with a bit of low-level code, it s possible to tweak the GridView s control hierarchy to create a more customized interface. In this tutorial we saw how to add a sort group separator row for a sortable GridView, which more easily identifies the distinct groups and those groups boundaries. For additional examples of customized sorting interfaces, check out Scott Guthrie s A Few ASP.NET 2.0 GridView Sorting Tips and Tricks blog entry.
Happy Programming!
About the Author
Scott Mitchell, author of seven ASP/ASP.NET books and founder of 4GuysFromRolla.com, has been working with Microsoft Web technologies since 1998. Scott works as an independent consultant, trainer, and writer. His latest book is Sams Teach Yourself ASP.NET 2.0 in 24 Hours. He can be reached at mitchell@4GuysFromRolla.com. or via his blog, which can be found at http://ScottOnWriting.NET.
 )
)
|
|





