Search
[!INCLUDETutorial Note]
Adding a Search Method and Search View
In this section you’ll add search capability to the Index action method that lets you search movies by genre or name.
Updating the Index Form
Start by updating the Index action method to the existing MoviesController class. Here’s the code:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Index(string searchString)
2: {
3: var movies = from m in db.Movies
4: select m;
5:
6: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
7: {
8: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
9: }
10:
11: return View(movies);
12: }
The first line of the Index method creates the following LINQ query to select the movies:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: var movies = from m in db.Movies
2: select m;
The query is defined at this point, but hasn’t yet been run against the database.
If the searchString parameter contains a string, the movies query is modified to filter on the value of the search string, using the following code:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
2: {
3: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
4: }
The s => s.Title code above is a Lambda Expression. Lambdas are used in method-based LINQ queries as arguments to standard query operator methods such as the Where method used in the above code. LINQ queries are not executed when they are defined or when they are modified by calling a method such as Where or OrderBy. Instead, query execution is deferred, which means that the evaluation of an expression is delayed until its realized value is actually iterated over or the ToList method is called. In the Search sample, the query is executed in the Index.cshtml view. For more information about deferred query execution, see Query Execution.
[!NOTE] The Contains method is run on the database, not the c# code above. On the database, Contains maps to SQL LIKE, which is case insensitive.
Now you can update the Index view that will display the form to the user.
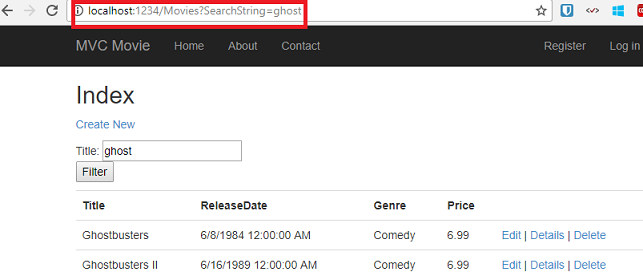
Run the application and navigate to /Movies/Index. Append a query string such as ?searchString=ghost to the URL. The filtered movies are displayed.

If you change the signature of the Index method to have a parameter named id, the id parameter will match the {id} placeholder for the default routes set in the App_Start.cs file.
[!code-jsonMain]
1: {controller}/{action}/{id}
The original Index method looks like this::
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Index(string searchString)
2: {
3: var movies = from m in db.Movies
4: select m;
5:
6: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
7: {
8: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
9: }
10:
11: return View(movies);
12: }
The modified Index method would look as follows:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Index(string id)
2: {
3: string searchString = id;
4: var movies = from m in db.Movies
5: select m;
6:
7: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
8: {
9: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
10: }
11:
12: return View(movies);
13: }
You can now pass the search title as route data (a URL segment) instead of as a query string value.

However, you can’t expect users to modify the URL every time they want to search for a movie. So now you you’ll add UI to help them filter movies. If you changed the signature of the Index method to test how to pass the route-bound ID parameter, change it back so that your Index method takes a string parameter named searchString:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Index(string searchString)
2: {
3: var movies = from m in db.Movies
4: select m;
5:
6: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
7: {
8: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
9: }
10:
11: return View(movies);
12: }
Open the Views.cshtml file, and just after @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create"), add the form markup highlighted below:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: @model IEnumerable<MvcMovie.Models.Movie>
2:
3: @{
4: ViewBag.Title = "Index";
5: }
6:
7: <h2>Index</h2>
8:
9: <p>
10: @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
11:
12: @using (Html.BeginForm()){
13: <p> Title: @Html.TextBox("SearchString") <br />
14: <input type="submit" value="Filter" /></p>
15: }
16: </p>
The Html.BeginForm helper creates an opening <form> tag. The Html.BeginForm helper causes the form to post to itself when the user submits the form by clicking the Filter button.
Visual Studio 2013 has a nice improvement when displaying and editing View files. When you run the application with a view file open, Visual Studio 2013 invokes the correct controller action method to display the view.

With the Index view open in Visual Studio (as shown in the image above), tap Ctr F5 or F5 to run the application and then try searching for a movie.

There’s no HttpPost overload of the Index method. You don’t need it, because the method isn’t changing the state of the application, just filtering data.
You could add the following HttpPost Index method. In that case, the action invoker would match the HttpPost Index method, and the HttpPost Index method would run as shown in the image below.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: [HttpPost]
2: public string Index(FormCollection fc, string searchString)
3: {
4: return "<h3> From [HttpPost]Index: " + searchString + "</h3>";
5: }
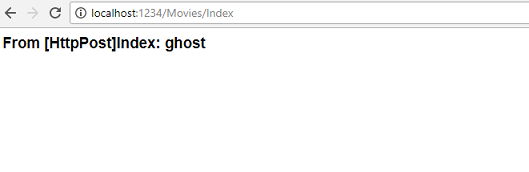
However, even if you add this HttpPost version of the Index method, there’s a limitation in how this has all been implemented. Imagine that you want to bookmark a particular search or you want to send a link to friends that they can click in order to see the same filtered list of movies. Notice that the URL for the HTTP POST request is the same as the URL for the GET request (localhost:xxxxx/Movies/Index) – there’s no search information in the URL itself. Right now, the search string information is sent to the server as a form field value. This means you can’t capture that search information to bookmark or send to friends in a URL.
The solution is to use an overload of BeginForm that specifies that the POST request should add the search information to the URL and that it should be routed to the HttpGet version of the Index method. Replace the existing parameterless BeginForm method with the following markup:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: @using (Html.BeginForm("Index","Movies",FormMethod.Get))
Now when you submit a search, the URL contains a search query string. Searching will also go to the HttpGet Index action method, even if you have a HttpPost Index method.
Adding Search by Genre
If you added the HttpPost version of the Index method, delete it now.
Next, you’ll add a feature to let users search for movies by genre. Replace the Index method with the following code:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Index(string movieGenre, string searchString)
2: {
3: var GenreLst = new List<string>();
4:
5: var GenreQry = from d in db.Movies
6: orderby d.Genre
7: select d.Genre;
8:
9: GenreLst.AddRange(GenreQry.Distinct());
10: ViewBag.movieGenre = new SelectList(GenreLst);
11:
12: var movies = from m in db.Movies
13: select m;
14:
15: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
16: {
17: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
18: }
19:
20: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(movieGenre))
21: {
22: movies = movies.Where(x => x.Genre == movieGenre);
23: }
24:
25: return View(movies);
26: }
This version of the Index method takes an additional parameter, namely movieGenre. The first few lines of code create a List object to hold movie genres from the database.
The following code is a LINQ query that retrieves all the genres from the database.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: var GenreQry = from d in db.Movies
2: orderby d.Genre
3: select d.Genre;
The code uses the AddRange method of the generic List collection to add all the distinct genres to the list. (Without the Distinct modifier, duplicate genres would be added — for example, comedy would be added twice in our sample). The code then stores the list of genres in the ViewBag.movieGenre object. Storing category data (such a movie genre’s) as a SelectList object in a ViewBag, then accessing the category data in a dropdown list box is a typical approach for MVC applications.
The following code shows how to check the movieGenre parameter. If it’s not empty, the code further constrains the movies query to limit the selected movies to the specified genre.
[!code-csharpMain]
1: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(movieGenre))
2: {
3: movies = movies.Where(x => x.Genre == movieGenre);
4: }
As stated previously, the query is not run on the data base until the movie list is iterated over (which happens in the View, after the Index action method returns).
Adding Markup to the Index View to Support Search by Genre
Add an Html.DropDownList helper to the Views.cshtml file, just before the TextBox helper. The completed markup is shown below:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: @model IEnumerable<MvcMovie.Models.Movie>
2: @{
3: ViewBag.Title = "Index";
4: }
5: <h2>Index</h2>
6: <p>
7: @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
8: @using (Html.BeginForm("Index", "Movies", FormMethod.Get))
9: {
10: <p>
11: Genre: @Html.DropDownList("movieGenre", "All")
12: Title: @Html.TextBox("SearchString")
13: <input type="submit" value="Filter" />
14: </p>
15: }
16: </p>
17: <table class="table">
In the following code:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: @Html.DropDownList("movieGenre", "All")
The parameter “movieGenre” provides the key for the DropDownList helper to find a IEnumerable<SelectListItem> in the ViewBag. The ViewBag was populated in the action method:
[!code-csharpMain]
1: public ActionResult Index(string movieGenre, string searchString)
2: {
3: var GenreLst = new List<string>();
4:
5: var GenreQry = from d in db.Movies
6: orderby d.Genre
7: select d.Genre;
8:
9: GenreLst.AddRange(GenreQry.Distinct());
10: ViewBag.movieGenre = new SelectList(GenreLst);
11:
12: var movies = from m in db.Movies
13: select m;
14:
15: if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
16: {
17: movies = movies.Where(s => s.Title.Contains(searchString));
18: }
19:
20: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(movieGenre))
21: {
22: movies = movies.Where(x => x.Genre == movieGenre);
23: }
24:
25: return View(movies);
26: }
The parameter “All” provides an option label. If you inspect that choice in your browser, you’ll see that its “value” attribute is empty. Since our controller only filters if the string is not null or empty, submitting an empty value for movieGenre shows all genres.
You can also set an option to be selected by default. If you wanted “Comedy” as your default option, you would change the code in the Controller like so:
[!code-cshtmlMain]
1: ViewBag.movieGenre = new SelectList(GenreLst, "Comedy");
Run the application and browse to /Movies/Index. Try a search by genre, by movie name, and by both criteria.

In this section you created a search action method and view that let users search by movie title and genre. In the next section, you’ll look at how to add a property to the Movie model and how to add an initializer that will automatically create a test database.
 )
)
|
|