Five amazing Linq-to-SQL extension (original in Ukrainian)
.NET Extension is a special .NET technology that looks like opposite of Class Inheritance. You can add a some function to static (or shared in VB.NET terminology) in base class. This is opportunity of language compilator, that transform high languages like VB or C# to MSIL, and programmers whose horizons are restricted С#, usually don't understand how to realize this function in VB.NET. Fist of all, VB have many advantage comparing simple languages like C# (for exmple see it in my page //www.vb-net.com/VB-Csharp-Difference/index.htm), one of this advantages is definition Module, that similar to mix as Namespace and static in C#. And in VB.NET Extension function is defined in Module code with special attribute System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension.
Extension function has difference to any another function in .NET, formally in definition (on C# or VB.NET) it has for one parameter greater than in run-time calling. This first parameter defines a base class, which static section is expanded with current extension function (in code below "T"). And definition of this class write in Generic-syntax (before first function parameters) - "(Of T as contraints)", where contrains defines interfaces, that can be necessary present in base class "T".
In my opinion Linq-to-SQL is best ORM in .NET framework stack. Commonly Microsoft create more and more method for manipulate data in memory buffer on high languages (evolution of MS method I I did listed in page //www.vb-net.com/DataAccessReview/index.htm and last technology of data manipulate (Entity Framework)is intended for fast change data base engine during program life cycle, and contains strange functional like mapper table name in memory to table name in DB engine and unfortunately not support main functional of any db engine like DB View (fully ignored that DB views is external presentation layer of simple normalized table of data). This disadvantage of Entity Framework and strange unclaimed functional of Entity Framework (like mapping many separate table column in memory to one table column in DB) increases the value of LINQ-TO-SQL as simple RAPID and very useful ORM among the general list of data access method for .NET framework (//www.vb-net.com/AspNetTechnologyStack/index.htm).
One of advantages of Linq-to-SQL is a simple expanding it for the extension function. LINQ-TO-SQL contains some alghorithms, that usually LINQ-TO-SQL manipulate of "Data.Linq.Table(Of T)", where defenition of "T" created automatically by Visual Studio by drag-and-drop from SQL Object Explorer. Below I show five amazing function on VB.NET, that expand Linq-to-SQL. But first of this function NewIfNull is very general and not directly related only to Linq-to-SQL. In this function "T" is defined as general class and this function expand any object in current packet of compilation.
1: Module LinqToSqlExtension0
2: ''' <summary>
3: ''' Create new object if it nothing (attention! parameters polimorphism not supported)
4: ''' </summary>
5: ''' <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
6: ''' <param name="value"></param>
7: ''' <param name="ParametersForNew">If object instance created without parameters, ParametersForNew may be omitted or may be nothing </param>
8: ''' <returns>return reference to object instance</returns>
9: ''' <remarks>(attention! parameters polimorphism not supported)</remarks>
10: <System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension()> _
11: Public Function NewIfNull(Of T As Class)(ByRef value As T, ByVal ParamArray ParametersForNew() As Object) As T
12: If value Is Nothing Then
13: Dim Types(0) As Type
14: Types(0) = GetType(T)
15: Dim ObjConstructors() As Reflection.ConstructorInfo = GetType(T).GetConstructors
16: If ParametersForNew Is Nothing Then
17: 'шукаємо CTOR без параметрів
18: For Each One In ObjConstructors
19: If One.GetParameters.Count = 0 Then
20: value = ObjConstructors(0).Invoke(ParametersForNew)
21: Return value
22: End If
23: Next
24: Throw New Exception("ParametersForNew is nothing, but constructor wihtout parameters is absent")
25: Else
26: Dim ParametersCount As Integer = ParametersForNew.Count
27: For i As Integer = 0 To ObjConstructors.Count - 1
28: If ObjConstructors(i).GetParameters.Count = ParametersCount Then
29: 'є конструктор, який має стільки ж параметрів, скілки передали у ParametersForNew
30: value = ObjConstructors(i).Invoke(ParametersForNew) 'Polimorphism not supported !!!
31: Return value
32: End If
33: Next
34: Throw New Exception("ParametersForNewhas " & ParametersCount & " parameters, but constructor with " & ParametersCount & " parameters with the same type is absent")
35: End If
36: Else
37: Return value
38: End If
39: End Function
40: End Module
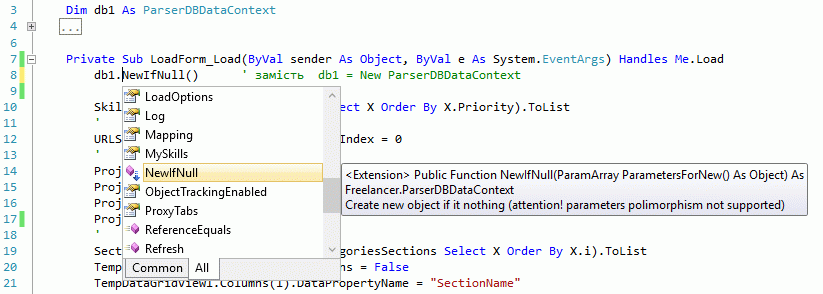
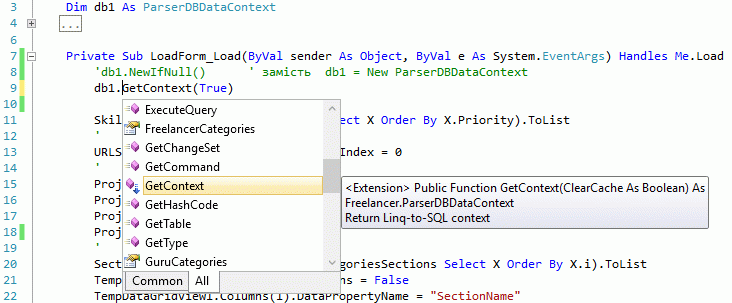
This function my apply to any objects in you program, including create DataContext of Linq-to-SQL and base page in ASP.NET. But in Linq-To-SQL there are one feature. If you use old DataContext, you have old cached data in DB, otherwise you need a new Linq-To-SQL datacontext. And below you may see a variant of this function specially fitted to LINQ-TO-SQL (with boolean parameter ClearCache).
1: Module LinqToSqlExtension4
2: ''' <summary>
3: ''' Return Linq-to-SQL context
4: ''' </summary>
5: ''' <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
6: ''' <param name="value"></param>
7: ''' <param name="ClearCache">True, if need clear cache</param>
8: ''' <returns>Linq-to-SQL context</returns>
9: <System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension()> _
10: Public Function GetContext(Of T As System.Data.Linq.DataContext)(ByRef value As T, ByVal ClearCache As Boolean) As T
11: If value IsNot Nothing And Not ClearCache Then
12: Return value
13: Else
14: 'create new
15: Dim ObjConstructors() As Reflection.ConstructorInfo = GetType(T).GetConstructors
16: 'шукаємо CTOR без параметрів
17: For Each One In ObjConstructors
18: If One.GetParameters.Count = 0 Then
19: value = ObjConstructors(0).Invoke(Nothing)
20: Return value
21: End If
22: Next
23: End If
24: End Function
25: End Module
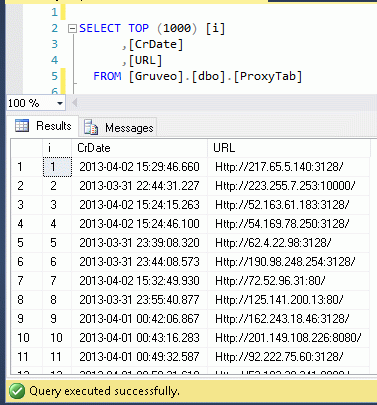
Most common operation with data in DB is update old data row or insert new row, if this data row is absent. Below you may see this operation in TSQL:
1: Create procedure UpdateURL
2: @URL as varchar (50)
3: as
4: IF NOT EXISTS (select 1 from [Gruveo].[dbo].[ProxyTab] where URL=@URL)
5: BEGIN
6: Insert [Gruveo].[dbo].[ProxyTab]
7: Values (GETDATE(),@URL)
8: END
9: ELSE
10: Update [Gruveo].[dbo].[ProxyTab]
11: set CrDate=GETDATE()
12: where URL=@URL
For example in this article I show this simple table of proxy-server. If ploxy-server is listed in this table, CrDate is update, otherwise new row with description of proxy-server is addind to this table.
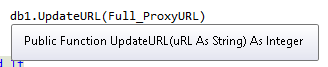
This Insert/Update pattern repeat many times from project to project and I finally I create extension for Linq-To-SQL that realize this pattern.
Alternate to this extension is a simple VB.NET code, like this:
1: Dim X As IEnumerable(Of ProxyTab) = (From Y In db1.ProxyTabs Select Y Where Y.URL = Full_ProxyURL).ToList
2: If X.Count = 0 Then
3: db1.ProxyTabs.InsertOnSubmit(New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL})
4: Else
5: For Each One As ProxyTab In X
6: One.CrDate = Now
7: Next
8: End If
This simple VB.CODE is easy to support and modifications, but if you have many-many fragment code, similar to this, you program is obstruct with this code template (with different table names and field names) and finally using a Linq-To-SQL extension has more benefits.
And below I show extension of Linq-To-SQL, that realized Insert operation of Insert/Update pattern of programming. This is a first simple function InsertIfNotExists:
1: Module LinqToSqlExtension1
2: ''' <summary>
3: ''' First prm - new record in table ;
4: ''' Second prm - checkng expression, that apply to table ;
5: ''' Return True if data inserted
6: ''' </summary>
7: ''' <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
8: ''' <param name="Table"></param>
9: ''' <param name="SelectPredicate">First prm - checking expression, appling to table, for example: Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL</param>
10: ''' <param name="NewEntity">Second prm - new record in table, for example: New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL}</param>
11: ''' <returns>Return True if data inserted</returns>
12: ''' <remarks>If Not db1.ProxyTabs.InsertIfNotExists(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL, New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL}) Then db1.ProxyTabs.UpdateForCondition(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL, Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now)</remarks>
13: <System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension()> _
14: Public Function InsertIfNotExists(Of T As Class)(ByVal Table As Data.Linq.Table(Of T),
15: ByVal SelectPredicate As Expressions.Expression(Of Func(Of T, Boolean)),
16: ByVal NewEntity As T) As Boolean
17: If Not Table.Any(SelectPredicate) Then
18: Table.InsertOnSubmit(NewEntity)
19: Table.Context.SubmitChanges()
20: Return True
21: Else
22: Return False
23: End If
24: End Function
25:
26: End Module
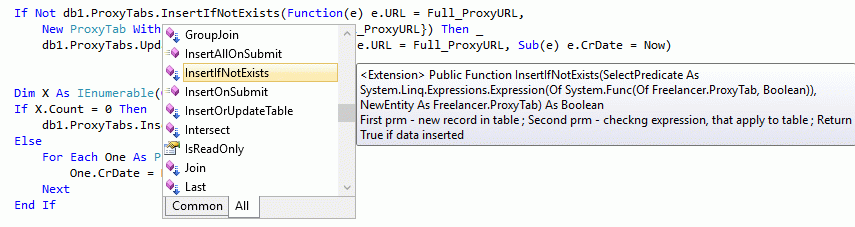
From now Insert-update template (that you seen twice above - in TSQL and simple VB.NET) will look as that:
1: If Not db1.ProxyTabs.InsertIfNotExists(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL,
2: New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL}) Then _
3: db1.ProxyTabs.UpdateForCondition(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL, Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now)
Commonly, it's a big questions, what code is more understandable - simple VB, TSQL or this execution of Linq-To-SQL extension function with Lambda Expression. But this calling to extension may be write in one string of VB.NET with different table and fields of table.
Pay attention that VB-compiler separating from this one string of VB-code one labda function, especially Lambda function "Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now" transform to hidden function _Lambda$__XXXX.
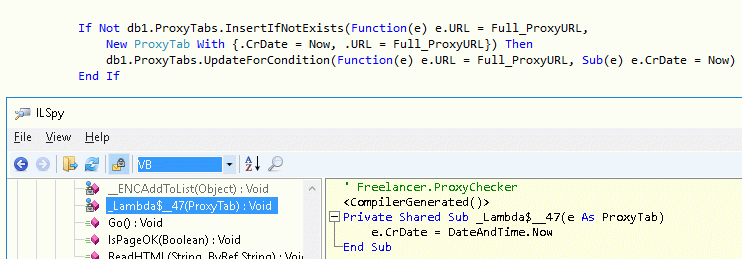
The secondary additionally function of insert-update pattern is UpdateForCondition:
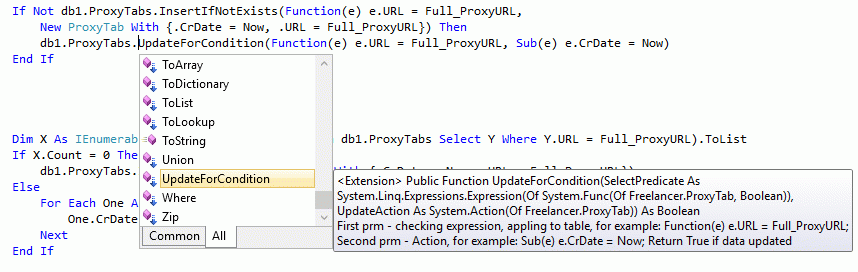
1: Module LinqToSqlExtension2
2: ''' <summary>
3: ''' First prm - checking expression, appling to table, for example: Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL;
4: ''' Second prm - Action, for example: Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now;
5: ''' Return True if data updated
6: ''' </summary>
7: ''' <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
8: ''' <param name="table"></param>
9: ''' <param name="SelectPredicate">First prm - checking expression, appling to table, for example: Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL</param>
10: ''' <param name="UpdateAction">Second prm - Action, for example: Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now</param>
11: ''' <returns>Return True if data updated</returns>
12: ''' <remarks>If Not db1.ProxyTabs.InsertIfNotExists(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL, New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL}) Then db1.ProxyTabs.UpdateForCondition(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL, Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now)</remarks>
13: <System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension()> _
14: Public Function UpdateForCondition(Of T As Class)(ByVal table As Data.Linq.Table(Of T),
15: ByVal SelectPredicate As Expressions.Expression(Of Func(Of T, Boolean)),
16: ByVal UpdateAction As Action(Of T)) As Boolean
17:
18: 'Dim X As IEnumerable(Of ProxyTab) = db1.ProxyTabs.Where(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL).ToList
19: 'For Each One As ProxyTab In SelectedRows
20: ' One.CrDate = Now
21: 'Next
22:
23: Dim SelectedRows As System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable(Of T) = table.Where(SelectPredicate)
24: If SelectedRows.Count > 0 Then
25: For Each One As T In SelectedRows
26: UpdateAction.Invoke(One)
27: Next
28: table.Context.SubmitChanges()
29: Return True
30: Else
31: Return False
32: End If
33: End Function
34:
35: End Module
And third function of insert-update pattern is InsertOrUpdateTable, that combine functional of both above function and consist fully realized of insert-update pattern.
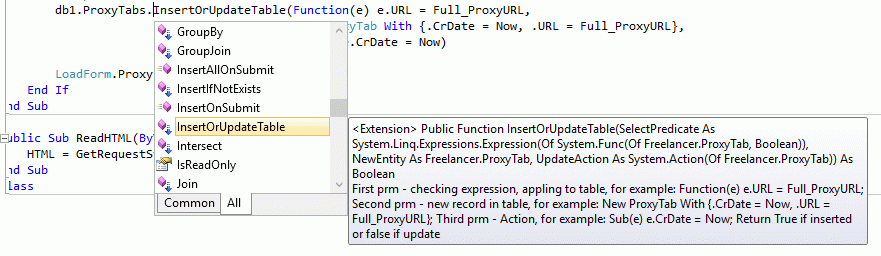
1: Module LinqToSqlExtension3
2: ''' <summary>
3: ''' First prm - checking expression, appling to table, for example: Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL;
4: ''' Second prm - new record in table, for example: New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL};
5: ''' Third prm - Action, for example: Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now;
6: ''' Return True if inserted or false if update
7: ''' </summary>
8: ''' <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
9: ''' <param name="Table"></param>
10: ''' <param name="SelectPredicate">First prm - checking expression, appling to table, for example: Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL</param>
11: ''' <param name="NewEntity">Second prm - new record in table, for example: New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL}</param>
12: ''' <param name="UpdateAction">Third prm - Action, for example: Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now</param>
13: ''' <returns>Return True if inserted or false if update</returns>
14: ''' <remarks>db1.ProxyTabs.InsertOrUpdateTable(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL, New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL}, Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now)</remarks>
15: <System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension()> _
16: Public Function InsertOrUpdateTable(Of T As Class)(ByVal Table As Data.Linq.Table(Of T),
17: ByVal SelectPredicate As Expressions.Expression(Of Func(Of T, Boolean)),
18: ByVal NewEntity As T,
19: ByVal UpdateAction As Action(Of T)) As Boolean
20: Dim SelectedRows As System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable(Of T) = Table.Where(SelectPredicate)
21: If SelectedRows.Count > 0 Then
22: For Each One As T In SelectedRows
23: UpdateAction.Invoke(One)
24: Next
25: Table.Context.SubmitChanges()
26: Return False
27: Else
28: Table.InsertOnSubmit(NewEntity)
29: Table.Context.SubmitChanges()
30: Return True
31: End If
32: End Function
33:
34: End Module
Execution of this function is show as this:
1: db1.ProxyTabs.InsertOrUpdateTable(Function(e) e.URL = Full_ProxyURL,
2: New ProxyTab With {.CrDate = Now, .URL = Full_ProxyURL},
3: Sub(e) e.CrDate = Now)
and this execution doing the same, as execution TSQL-procedure UpdateURL.