Why Microsoft vilified Visual Basic ?
I see a simple reason. Because VB based on C# syntax (C was born in 1978), VB is improving C ancient syntax for RAPID development, in VB we newer will use "+" as adding integer value, as concatenate string and even adding event to class, this is full different conception. In VB we newer use stupid char ";", we newer use reversy to you mind syntax, we newer use ":" as Implement and Inherit keyword simultaneously, this is full different conception in VB, but even experienced C# always confused in this simplest sentences, in VB we always operate with address in memory as address due to keyword AddressOF, in VB we newer confuse what is Delegate, what in Event (because we use keyword AddHandler, Handles and RaiseEvent), any C# programmer differ one this simple one from another with big difficulties. In other side in C# absolutely similar stuff as Property and Method without parameters we can perform with parentheses or without it. Simple idea as dynamic variable was exist since VB was born but this simplest stuff is appear only in last version of stupid C# syntax. In VB Lambda-expression is simplest conception because you always can replace Lambda to AddressOF another function, you always understand difference what is Address of something and what is calling something in memory address, but how is possible to aware what is "=>"? There are thousands improvements, I have no time to enumerate them.
Microsoft said that sour cream and shit from pan is the same, because they has the same fat content and sugar content. No, sorry, VB programmer understand differences between shit and cream, between stupid ancient C syntax and improving this shit syntax in VB.NET. And VB programmers always have understanding reason of Microsoft point of view - big goal of Microsoft is increase price of software in whole world, and than increase MS stock in stock market as leader of software development company. Because in practice VB program can easier for understanding, for example I have program with 300,000 and 600,000 string of my VB code and this my program is still easy to understand by other VB programmer, is any C# programmer can understand 25,000 string of code from other C# programmer?. VB programmer can create program in 10 times faster and cheaper than the same program in C# (look to any freelance venue as proof), but this price reduce of any program in whole world is fully rejected by Microsoft, than MS return to stupid C syntax from 1978 year.
C# programmers is always "follow the rules" programmers, Microsoft rules, rules to increase price of any program. C# programmers has special kind of mind that always obey to any Microsoft rules, master-slave pattern of their mind and relation to Microsoft point of view never can them create really good programs, only programs with maximum price.
For example look to the starting ASP.NET Core application at all, especially in DI container and what first page will be selected to start. If you have write in Classic APS.NET you sure that common environment to start and first page is pretty simple. You need to know nothing rather than - first page is Default.aspx (this page is defined in web server or in Visaul Studio). And all common environment is defined in global.asax. Nothing other you must be know. Even routing concept is too much, need only write a couple string of code in global.asax (like in the bottom of this page ASP.NET URL rewriting and thats is. Nothing else you need to know.
If you want create more sophisticated web site, you have various opportunity to create page dynamically - for example in this way SPA-page на Classic ASP.NET та jQuery. or use UpdatePanel techniques, like in this page Долгоиграющие странички с прогресс-баром.. Since 2002 year, since ASP.NET was born, you also can use WebAPI How classic ASP.NET programmers has realized WEB.API since 2005 year and also we could create page in asynchronous way and even first ORM (Linq-to-SQL) was born - Асинхронные странички. All this task was be extremely simple in Classic ASP.NET and 15 year ago we can create for one day the same site what we can create today during a month or more.
Than Microsoft done one-by-one some important steps:
- Delete WYSIWYG editor in Visual Studio.
- Delete opportunity to automatically create for Visual Studio event handler by one click on HTML-element.
- Entering "routing concept" instead simple analyze request URL and redirect to needed page by one string of code.
- Entering DI-container concept, after that one string of core was be transform to 100 string of code - I have some description of project in what 5 string of code was be transform to 500 string of code after adding DI-container Застосування патерну Dependency Injection за допомогою IoC-контейнера Ninject
- When Classic ASP.NET Technology was born, Micrisoft was said that "spaghetti code" with mix code and HTML is most stupid and slow to programming and understanding techniques. But now Microsoft forgot own main point and main reason to create ASP.NET technology and said - no-no-no, spaghetti code is good and right.
- Deleted in Blazor technology jQuery, because so many programmer know and love that library.
- C# was born in 1978, than for many years it was be improved, because program writing programmer to programmer, not to machine. As a resolt of this movement Visual Basic was born, as special language for simple and RAPID programming. But now Microsoft said, no-no-no, this languages too simple and too faster for programming. No-no-no, this is not our way, our goal is programmer who create one simple site during whole life - Why Microsoft vilified Visual Basic ?
- MS added in Visual Studio spyware and now MS has information about any tiny programmer operation in whole world. Also NET Core has spyware so named "Hosting diagnostic". This is second big Microsoft dream - collect all information about all peoples in whole world. And what we have as a result? In 1999 year I was worked in Celeron-100 Computer with 128M memory in Visual Basic 6. That computer was working instantly, I never wait even one second. Now I work in Core I5 processor with 8GB Memory. And even I doing simplest oiperation like copy-past I always waiting at least one second.
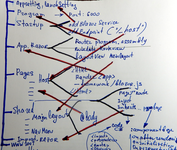
And what we have as common result of Microsoft efforts? What this bull is achieve in IT industry? W Why now we need a month to create the same site was created 15 year ago during one day? Look at scheme below - this is configuring process of start Blazor application and selecting start page. Instead nothing in Classic ASP.NET.
Do I wait anything from MS? Yes, one important step will be repair MS reputation for me. If MS will said - Yes, we agree mistake, C# is too stupid and ancient syntax for programming, we newer will use it again. We will return to RAPID style of programming, for human-like language for programming and in future we always support only B# language based on VB.NET.
About 0,5 million peoples write in VB.NET full automatically, without thinking at all, like breathing, and doing this 25+ years, but ... MS create new languages F# instead support VB.NET further. After huge efforts and spent a lot of money for advertise only 10 thousand peoples try to use that scrap. Why MS doing this terrible thing? No answer other, than obvious to me. VB.NET is too fast, too successful and software has low price for end-user, therefore VB.NET forbidden by Microsoft.
And look to my VB-C# comparing below, and try to understand what is language for professionals and what is scrap for beginners?
- VB use more advanced OOP conception, for example Shadowing, Module. Enums, for example can be defined inside interfaces. Implements and Inherits is full different conception in VB, in VB we never use one char ":" to define both of it. In VB.NET we never be confused what difference between inheritance from abstract class and interface implementation. In other side similar thing (like property and method without parameters) call in C# by full different way.
- VB use remarkable and understandable manipulation of events and delegates AddHandler , RemoveHandler, Event, WithEvents, RaiseEvents, AddressOF, Handles. If you use Event declaration, in VB delegates declare automatically and exemplar of delegetes will be create automatically, you can use manual delegate declaration only if it needed. In VB.NET we never be confused what in events and what is delegate, we never manipulate eventhandler as digital by char "+" because this is full different entity and each of it has remarkable and different keywords.
- VB has alternative exception concept, for example Resume Next. This is convenient way of process exception for example in ASP page and VBA program.
- VB has advanced future for Array manipulation like ReDim
- VB has default Namespace for whole project, no need to use at all this conception at all. Assembly name, OOP, extension, partial class definition and so on is full enough to build any complexity system.
- All needed to programing type conversion and string manipulation function is part of VB.NET, VB function LIKE is more simple and useful than Regular expression.
- Interaction with user like read input or show message is part of VB. Many other part of .NET Framework (for example working for Files, Registry, Color, Memory dispose and so on) also is domestic parts of VB.NET. All environment of your program (including network card, memory, videoadapter) you can see and check in class My. You can use any of this function independently of used NET.Framework version.
- Various most usable in practice type checking function like (IsNothing, IsNumeric, IsDbNull and so on) is domestic part of VB.NET and you can use it independently from current version of .NET Framework. Also various useful constant as VbCrLF and VbTab is part of languages. All you need for simple desktop program - you always have inside languages, this is benefits for beginners to immediately start programming and make code short and amazing.
- VB can compare string globally as case sensitive or insensitive. This is two different historical culture - Windows and Linux and you can once define type of string comparison in compiler options.
- Various mathematical operation like Raise in power and more advanced is part of VB.NET.
- No need to write dump spell "return null" if you can not make needed operation in function, return null will be attaching automatically. And you can use "End" to full stop execution of your program.
- A lot of other statement, despite the similar name to C#, like Tuples in VB working differently.
- in VB you can a lot various keywords (absent in C#) to help other programmer understand what exactly you doing, for example ByVal parameters modifier. Instead this C# has a lot of mindless ritual spell, for example {get;set;} in short form of property declaration.
- In VB we never use the same characters for full different thing, for example if you want concatenate string you can use "&", if you want adding numeric value you can use "+", if you can add event handler you can attach it statically by Handles or dynamically by AddHandler. For all this different thing you must use in C# only "+". Even full opposite idea as implementation and inheritance in C# you must use the same character ":". And in VB you never denote the same thing by different way, for example what difference between method without parameters and property? But in C# one perform with "()" and second without "()".
- VB languages is case insensitive, this is one or research result to transform ancient C syntax to RAPID programming languages. Since VB4 environment and VBA for Excel VB.NET programmer declare variable in UpperCamelCase and type in program body variables in lowCamelCase. If variables and keywords is recognized successfully by IDE, IDE immediately кфшіу up first letter, make first letter capital. Also VB compiler is more intellectual, no need type dump character ";" after each line.
- Other result of research to improve stupid C syntax is follow human mind pattern, "var X" ("Dim X as string") is native human way to thinking, not "(string) x;", i.e in VB.NET you never use inverse pattern of your mind thinking.
- #if, #else, #elif, #endif
- #define, #undef
- #warning, #error
- #line
- #region, #endregion
- #pragma, #pragma warning, #pragma checksum
NameSpace
- ::
- Default namespace is absent in C#
- Namespace in project bind to location in C# project
Control flow
- Selection statements:
- Iteration statements:
- Jump statements:
- Exception handling statements:
- throw
- try-catch
- try-finally
- try-catch-finally
- On Error Resume Next is absent in C#
- Other control flow statement like With, End With,
Resume Exit For, Sub, Exit Sub, Loop, Stop etc is absent in C#
Events/delegates
- delegate, invoke delegate as method ()
- += (AddHandler)
- -= (RemoveHandler)
- Any functions of Events/Delegates like Event, WithEvents, RaiseEvents, AddressOF, Handles forbidden in C#
- 1 bytes:
- 2 bytes:
- 4 bytes:
- 8 bytes:
- 16 bytes:
- ref:
- val:
- string:
- literal:
Adding string, numeric, float, delegate
- -=, +=
- instead AddHandler, RemoveHandler, &=
Compare
Null (Nothing)
- ?? (IF, Is Nothing, Is NotNothing)
- ?. or ?[]
- !
- Other information as
IsDbNull, IsNothing is absent in C#
in C# is absent:
- ByRef and ByVal parameters modifier
- Widening and Narrowing conversion
- Literal Data Types
- XML Literals
- Datetime literal like #12/31/2020#
- ParamArray parameter
- Key for Anonymous function
- IsNumeric, IsArray, IsReference etc
- public
- protected
- internal (Friend)
- private
- protected internal
- private protected
- const
- readonly
- partial
- Iterator, Shadow keywords missing in C#
Instantiate
OOP keywords
- : (Inherits), : (Implements)
- sealed (NonInheritable)
- static (Shared)
- virtual (Overridable)
- abstract # (MustInherit MustOverride)
- override (Overloading or Overriding)
- Any other OOP opportunity Assembly
( Module, Shadows, Overloads) forbidden in C#
Type check and conversion
- ()
- as
- is (Is) true if an instance is in the inheritance tree
- typeof type name at compile time
- GetType (GetType) runtime type of an instance
- ? NotNullWhen
In C# is absent built-in conversion
- TryCast and CType keywords
- Cint, Cbool etc. conversion
- Float point Fix conversion
- Ascii/Unicode conversion ChrW, Chr, Asc, AscW
- Number/String conversion Format, Str, Val, Hex, Oct
- Upper/Lower case conversion UCase, LCase
- Date and Time conversion DateSerial, DateValue, TimeSerial, TimeValue, Day, Month, Weekday, Year, Hour, Minute, Second
- this (Me or MyClass)
- base (MyBase)
- value
- nameof
- sizeof
- default
- ref #
- switch
- Linq keywords has another order
MultiThreading
Generic
Pointer operators
Logical and bitwise
- && (AndAlso)
- || (OrElse)
- & (And)
- | (Or)
- ^ (Xor)
- ! (Not)
- ~ (Xor)
- <<(<<)
- >>(>>)
- & (And)
- | (Or)
- Eqv and Imp is absent in C#
Array access
Math operation
- volatile (MTAThread)
- extern (DllImport) Unicode or Ansi modifier, Alias is absent
- C# compiler options
- Option Strict, Option Compare, Option Explicit, Option Infer is absent
In C# is absent
- Any I/O function FileOpen, FileClose, Reset, Format, Print, SPC, TAB, FileWidth, FileCopy, EOF, FileAttr, FileDateTime, FileLen, FreeFile, GetAttr, Loc, LOF, Seek, InputBox, MsgBox, Dir, Kill, Lock, Unlock, FileGet, FileGetObject, Input, InputString, LineInput, FileLen, FileAttr, GetAttr, SetAttr, Seek, FilePut, FilePutObject, Print, Write, WriteLine
- Any financial function DDB, SLN, SYD, FV, Rate, IRR, MIRR, NPer, IPmt, Pmt, PPmt, NPV, PV
- Any XML function
- Any Registry statement DeleteSetting, GetSetting, GetAllSettings, SaveSetting
- Any user Interaction statement InputBox, MsgBox, Beep
- Any string manipulation statement StrComp, StrConv, InStrRev, StrReverse, Format, LCase, UCase, Space, StrDup, Len, Format, FormatCurrency, FormatDateTime, FormatNumber, FormatPercent, InStr, Left, LTrim, Mid, Right, RTrim, Trim, Option Compare, Asc, AscW, Chr, ChrW, Replace, Filter, Split, Join
- A lot of other statement Collection, AppActivate, Shell, CallByName, Command, CreateObject, GetObject, QBColor, RGB and so on is abcent in C# at all.
| VB.NET (2005), (2010), (2015), (2017), (2020) | C# (2020) |
|---|---|
| Program Structure | |
1: Imports System 2:
3: Namespace Hello 4: Class HelloWorld 5: Overloads Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String) 6: Dim name As String = "VB.NET" 7:
8: 'See if an argument was passed from the command line 9: If args.Length = 1 Then name = args(0) 10:
11: Console.WriteLine("Hello, " & name & "!") 12: End Sub 13: End Class 14: End Namespace |
1: using System; 2:
3: namespace Hello { 4: public class HelloWorld { 5: public static void Main(string[] args) { 6: string name = "C#"; 7:
8: // See if an argument was passed from the command line 9: if (args.Length == 1) 10: name = args[0];
11: Console.WriteLine("Hello, " + name + "!"); 12: }
13: }
14: }
|
| Comments | |
1: ' Single line only 2:
3: REM Single line only 4:
5: ''' <summary>XML comments</summary> |
1: // Single line 2: /* Multiple 3: line */ 4: /// <summary>XML comments on single line</summary> 5: /** <summary>XML comments on multiple lines</summary> */ |
| Data Types | |
1: 'Value Types 2: Boolean 3: Byte, SByte 4: Char 5: Short, UShort, Integer, UInteger, Long, ULong 6: Single, Double 7: Decimal 8: Date (alias of System.DateTime) 9: structures 10: enumerations 11:
12: 'Reference Types 13: objects 14: String 15: arrays 16: delegates 17:
18: 'Initializing 19: Dim correct As Boolean = True 20: Dim b As Byte = &H2A 'hex or &O52 for octal 21: Dim person As Object = Nothing 22: Dim name As String = "Dwight" 23: Dim grade As Char = "B"c 24: Dim today As Date = #12/31/2010 12:15:00 PM# 25: Dim amount As Decimal = 35.99@ 26: Dim gpa As Single = 2.9! 27: Dim pi As Double = 3.14159265 28: Dim lTotal As Long = 123456L 29: Dim sTotal As Short = 123S 30: Dim usTotal As UShort = 123US 31: Dim uiTotal As UInteger = 123UI 32: Dim ulTotal As ULong = 123UL 33:
34: 'Nullable Types 35: Dim x? As Integer = Nothing 36:
37: 'Anonymous Types 38: Dim stu = New With {.Name = "Sue", .Gpa = 3.4} 39: Dim stu2 = New With {Key .Name = "Bob", .Gpa = 2.9} 40:
41: 'Implicitly Typed Local Variables 42: Dim s = "Hello!" 43: Dim nums = New Integer() {1, 2, 3} 44: Dim hero = New SuperHero With {.Name = "Batman"} 45:
46: 'Type Information 47: Dim x As Integer 48: Console.WriteLine(x.GetType()) ' System.Int32 49: Console.WriteLine(GetType(Integer)) ' System.Int32 50: Console.WriteLine(TypeName(x)) ' Integer 51:
52: Dim c as New Circle 53: isShape = TypeOf c Is Shape ' True if c is a Shape 54: isSame = o1 Is o2 // True if o1 and o2 reference same object 55:
56: 'Type Conversion / Casting 57: Dim d As Single = 3.5 58: Dim i As Integer = CType(d, Integer) ' set to 4 (Banker's rounding) 59: i = CInt(d) ' same result as CType 60: i = Int(d) ' set to 3 (Int function truncates the decimal) 61:
62: Dim s As New Shape 63: Dim c As Circle = TryCast(s, Circle) ' Returns Nothing if type cast fails 64: c = DirectCast(s, Circle) ' Throws InvalidCastException if type cast fails |
1: //Value Types 2: bool 3: byte, sbyte 4: char 5: short, ushort, int, uint, long, ulong 6: float, double 7: decimal 8: DateTime (not a built-in C# type) 9: structs 10: enumerations 11:
12: //Reference Types 13: objects 14: string 15: arrays 16: delegates 17:
18: //Initializing 19: bool correct = true; 20: byte b = 0x2A; // hex 21: object person = null; 22: string name = "Dwight"; 23: char grade = 'B'; 24: DateTime today = DateTime.Parse("12/31/2010 12:15:00 PM"); 25: decimal amount = 35.99m; 26: float gpa = 2.9f; 27: double pi = 3.14159265; // or 3.14159265D 28: long lTotal = 123456L; 29: short sTotal = 123; 30: ushort usTotal = 123; 31: uint uiTotal = 123; // or 123U 32: ulong ulTotal = 123; // or 123UL 33:
34: //Nullable Types 35: int? x = null; 36:
37: //Anonymous Types 38: var stu = new {Name = "Sue", Gpa = 3.5}; 39: var stu2 = new {Name = "Bob", Gpa = 2.9}; // no Key equivalent 40:
41: //Implicitly Typed Local Variables 42: var s = "Hello!"; 43: var nums = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; 44: var hero = new SuperHero() { Name = "Batman" }; 45:
46: //Type Information 47: int x; 48: Console.WriteLine(x.GetType()); // System.Int32 49: Console.WriteLine(typeof(int)); // System.Int32 50: Console.WriteLine(x.GetType().Name); // Int32 51:
52: Circle c = new Circle(); 53: isShape = c is Shape; // true if c is a Shape 54:
55: isSame = Object.ReferenceEquals(o1, o2) // true if o1 and o2 reference same object 56:
57: //Type Conversion / Casting 58: float d = 3.5f; 59: i = Convert.ToInt32(d); // Set to 4 (rounds) 60: int i = (int)d; // set to 3 (truncates decimal) 61:
62: Shape s = new Shape(); 63: Circle c = s as Circle; // Returns null if type cast fails 64: c = (Circle)s; // Throws InvalidCastException if type cast fails |
| Constants | |
1: Const MAX_STUDENTS As Integer = 25 2:
3: ' Can set to a const or var; may be initialized in a constructor 4: ReadOnly MIN_DIAMETER As Single = 4.93 |
1: const int MAX_STUDENTS = 25; 2:
3: // Can set to a const or var; may be initialized in a constructor 4: readonly float MIN_DIAMETER = 4.93f; |
| Enumerations | |
1: Enum Action 2: Start
3: [Stop] ' Stop is a reserved word 4: Rewind
5: Forward
6: End Enum 7:
8: Enum Status 9: Flunk = 50
10: Pass = 70
11: Excel = 90
12: End Enum 13:
14: Dim a As Action = Action.Stop 15: If a <> Action.Start Then _ 16: Console.WriteLine(a.ToString & " is " & a) ' "Stop is 1" 17:
18: Console.WriteLine(Status.Pass) ' 70 19: Console.WriteLine(Status.Pass.ToString) ' Pass
|
1: enum Action {Start, Stop, Rewind, Forward}; 2: enum Status {Flunk = 50, Pass = 70, Excel = 90}; 3:
4: Action a = Action.Stop;
5: if (a != Action.Start) 6: Console.WriteLine(a + " is " + (int) a); // "Stop is 1" 7:
8: Console.WriteLine((int) Status.Pass); // 70 9: Console.WriteLine(Status.Pass); // Pass |
| Operators | |
1: 'Comparison 2: = < > <= >= <>
3:
4: 'Arithmetic 5: + - * /
6: Mod 7: \ (integer division) 8: ^ (raise to a power) 9:
10: 'Assignment 11: = += -= *= /= \= ^= <<= >>= &=
12:
13: 'Bitwise 14: And Or Xor Not << >> 15:
16: 'Logical 17: AndAlso OrElse And Or Xor Not 18:
19: 'Note: AndAlso and OrElse perform short-circuit logical evaluations 20:
21: 'String Concatenation 22: &
|
1: //Comparison 2: == < > <= >= !=
3:
4: //Arithmetic 5: + - * /
6: % (mod)
7: / (integer division if both operands are ints) 8: Math.Pow(x, y)
9:
10: //Assignment 11: = += -= *= /= %= &= |= ^= <<= >>= ++ --
12:
13: //Bitwise 14: & | ^ ~ << >>
15:
16: //Logical 17: && || & | ^ !
18:
19: //Note: && and || perform short-circuit logical evaluations 20:
21: //String Concatenation 22: +
|
| Choices | |
1: ' Null-coalescing operator if called with 2 arguments 2: x = If(y, 5) ' if y is not Nothing then x = y, else x = 5 3:
4: ' Ternary/Conditional operator (IIf evaluates 2nd and 3rd expressions) 5: greeting = If(age < 20, "What's up?", "Hello") 6:
7: ' One line doesn't require "End If" 8: If age < 20 Then greeting = "What's up?" 9: If age < 20 Then greeting = "What's up?" Else greeting = "Hello" 10:
11: ' Use : to put two commands on same line 12: If x <> 100 AndAlso y < 5 Then x *= 5 : y *= 2 13:
14: ' Preferred 15: If x <> 100 AndAlso y < 5 Then 16: x *= 5
17: y *= 2
18: End If 19:
20: ' Use _ to break up long single line or use implicit line break 21: If whenYouHaveAReally < longLine And 22: itNeedsToBeBrokenInto2 > Lines Then _ 23: UseTheUnderscore(charToBreakItUp)
24:
25: 'If x > 5 Then 26: x *= y
27: ElseIf x = 5 OrElse y Mod 2 = 0 Then 28: x += y
29: ElseIf x < 10 Then 30: x -= y
31: Else 32: x /= y
33: End If 34:
35: Select Case color ' Must be a primitive data type 36: Case "pink", "red" 37: r += 1
38: Case "blue" 39: b += 1
40: Case "green" 41: g += 1
42: Case Else 43: other += 1
44: End Select |
1: // Null-coalescing operator 2: x = y ?? 5; // if y != null then x = y, else x = 5 3:
4: // Ternary/Conditional operator 5: greeting = age < 20 ? "What's up?" : "Hello"; 6:
7: if (age < 20) 8: greeting = "What's up?"; 9: else 10: greeting = "Hello"; 11:
12: // Multiple statements must be enclosed in {} 13: if (x != 100 && y < 5) { 14: x *= 5;
15: y *= 2;
16: }
17:
18:
19: No need for _ or : since ; is used to terminate each statement. 20:
21:
22:
23: if (x > 5) 24: x *= y;
25: else if (x == 5 || y % 2 == 0) 26: x += y;
27: else if (x < 10) 28: x -= y;
29: else 30: x /= y;
31:
32:
33:
34: // Every case must end with break or goto case 35: switch (color) { // Must be integer or string 36: case "pink": 37: case "red": r++; break; 38: case "blue": b++; break; 39: case "green": g++; break; 40: default: other++; break; // break necessary on default 41: }
|
| Loops | |
1: 'Pre-test Loops: 2: While c < 10 3: c += 1
4: End While 5:
6: Do Until c = 10 7: c += 1
8: Loop 9:
10: Do While c < 10 11: c += 1
12: Loop 13:
14: For c = 2 To 10 Step 2 15: Console.WriteLine(c)
16: Next 17:
18: 'Post-test Loops: 19: Do 20: c += 1
21: Loop While c < 10 22:
23: Do 24: c += 1
25: Loop Until c = 10 26:
27: ' Array or collection looping 28: Dim names As String() = {"Fred", "Sue", "Barney"} 29: For Each s As String In names 30: Console.WriteLine(s)
31: Next 32:
33: ' Breaking out of loops 34: Dim i As Integer = 0 35: While (True) 36: If (i = 5) Then Exit While 37: i += 1
38: End While 39:
40: ' Continue to next iteration 41: For i = 0 To 4 42: If i < 4 Then Continue For 43: Console.WriteLine(i) ' Only prints 4 44: Next |
1: //Pre-test Loops: 2:
3: // no "until" keyword 4: while (c < 10)
5: c++;
6:
7:
8: for (c = 2; c <= 10; c += 2) 9: Console.WriteLine(c);
10:
11:
12:
13:
14:
15:
16:
17:
18: //Post-test Loop: 19:
20: do 21: c++;
22: while (c < 10);
23:
24:
25: // Array or collection looping 26: string[] names = {"Fred", "Sue", "Barney"}; 27: foreach (string s in names) 28: Console.WriteLine(s);
29:
30:
31: // Breaking out of loops 32: int i = 0; 33: while (true) { 34: if (i == 5) 35: break; 36: i++;
37: }
38:
39: // Continue to next iteration 40: for (i = 0; i <= 4; i++) { 41: if (i < 4) 42: continue; 43: Console.WriteLine(i); // Only prints 4 44: }
|
| Arrays | |
1: Dim nums() As Integer = {1, 2, 3} 2: For i As Integer = 0 To nums.Length - 1 3: Console.WriteLine(nums(i))
4: Next 5:
6: ' 4 is the index of the last element, so it holds 5 elements 7: Dim names(4) As String 8: names(0) = "David" 9: names(5) = "Bobby" ' Throws System.IndexOutOfRangeException 10:
11: ' Resize the array, keeping the existing values (Preserve is optional) 12: ReDim Preserve names(6) 13:
14: Dim twoD(rows-1, cols-1) As Single 15: twoD(2, 0) = 4.5
16:
17: Dim jagged()() As Integer = { _ 18: New Integer(4) {}, New Integer(1) {}, New Integer(2) {} } 19: jagged(0)(4) = 5
|
1: int[] nums = {1, 2, 3}; 2: for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++) 3: Console.WriteLine(nums[i]);
4:
5:
6: // 5 is the size of the array 7: string[] names = new string[5]; 8: names[0] = "David"; 9: names[5] = "Bobby"; // Throws System.IndexOutOfRangeException 10:
11: // Add two elements, keeping the existing values 12: Array.Resize(ref names, 7); 13:
14: float[,] twoD = new float[rows, cols]; 15: twoD[2,0] = 4.5f;
16:
17: int[][] jagged = new int[3][] { 18: new int[5], new int[2], new int[3] }; 19: jagged[0][4] = 5;
|
| Collections | |
1: ' Popular classes in System.Collections (stored as Object) 2: ArrayList
3: Hashtable
4: Queue
5: Stack
6:
7: 'Popular classes in System.Collections.Generic (stored as type T) 8: List(Of T)
9: SortedList(Of TKey, TValue)
10: Dictionary(Of TKey, TValue)
11: Queue(Of T)
12: Stack(Of T)
13:
14: 'Popular classes in System.Collections.Concurrent (thread safe) 15: BlockingCollection(Of T)
16: ConcurrentDictionary(Of TKey, TValue)
17: ConcurrentQueue(Of T)
18: ConcurrentStack(Of T)
19:
20: 'Microsoft.VisualBasic (not recommended) 21: Collection
22:
23:
24: ' Store ID and name 25: Dim students As New Dictionary(Of Integer, String) From 26: {
27: {123, "Bob"}, 28: {444, "Sue"}, 29: {555, "Jane"} 30: }
31:
32: students.Add(987, "Gary") 33: Console.WriteLine(students(444)) ' Sue 34:
35: ' Display all 36: For Each stu In students 37: Console.WriteLine(stu.Key & " = " & stu.Value) 38: Next 39:
40: ' Method iterator for custom iteration over a collection 41: Iterator Function OddNumbers(ByVal lastNum As Integer) As System.Collections.IEnumerable 42: For num = 1 To lastNum 43: If num Mod 2 = 1 Then 44: Yield num
45: End If 46: Next 47: End Function 48:
49: ' 1 3 5 7 50: For Each num In OddNumbers(7) 51: Console.Write(num & " ") 52: Next
|
1: // Popular classes in System.Collections (stored as Object) 2: ArrayList
3: Hashtable
4: Queue
5: Stack
6:
7: //Popular classes in System.Collections.Generic (stored as type T) 8: List<T>
9: SortedList<TKey, TValue>
10: Dictionary<TKey, TValue>
11: Queue<T>
12: Stack<T>
13:
14: //Popular classes in System.Collections.Concurrent (thread safe) 15: BlockingCollection<T>
16: ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>
17: ConcurrentQueue<T>
18: ConcurrentStack<T>
19:
20: //No equivalent to Microsoft.VisualBasic.Collection 21:
22:
23: // Store ID and name 24: var students = new Dictionary<int, string> 25: {
26: { 123, "Bob" }, 27: { 444, "Sue" }, 28: { 555, "Jane" } 29: };
30:
31: students.Add(987, "Gary"); 32: Console.WriteLine(students[444]); // Sue 33:
34: // Display all 35: foreach (var stu in students) { 36: Console.WriteLine(stu.Key + " = " + stu.Value); 37: }
38:
39:
40: // Method iterator for custom iteration over a collection 41: static System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<int> OddNumbers(int lastNum) 42: {
43: for (var num = 1; num <= lastNum; num++) 44: if (num % 2 == 1) 45: yield return num; 46: }
47:
48: // 1 3 5 7 49: foreach (double num in OddNumbers(7)) 50: {
51: Console.Write(num + " "); 52: }
|
| Functions | |
1: ' Pass by value (in, default), reference (in/out), and reference (out) 2: Sub TestFunc(ByVal x As Integer, ByRef y As Integer, ByRef z As Integer) 3: x += 1
4: y += 1
5: z = 5
6: End Sub 7:
8: Dim a = 1, b = 1, c As Integer ' c set to zero by default 9: TestFunc(a, b, c)
10: Console.WriteLine("{0} {1} {2}", a, b, c) ' 1 2 5 11:
12: ' Accept variable number of arguments 13: Function Sum(ByVal ParamArray nums As Integer()) As Integer 14: Sum = 0
15: For Each i As Integer In nums 16: Sum += i
17: Next 18: End Function ' Or use Return statement like C# 19:
20: Dim total As Integer = Sum(4, 3, 2, 1) ' returns 10 21:
22: ' Optional parameters must be listed last and must have a default value 23: Sub SayHello(ByVal name As String, Optional ByVal prefix As String = "") 24: Console.WriteLine("Greetings, " & prefix & " " & name) 25: End Sub 26:
27: SayHello("Strangelove", "Dr.") 28: SayHello("Mom") |
1: // Pass by value (in, default), reference (in/out), and reference (out) 2: void TestFunc(int x, ref int y, out int z) { 3: x++;
4: y++;
5: z = 5;
6: }
7:
8: int a = 1, b = 1, c; // c doesn't need initializing 9: TestFunc(a, ref b, out c); 10: Console.WriteLine("{0} {1} {2}", a, b, c); // 1 2 5 11:
12: // Accept variable number of arguments 13: int Sum(params int[] nums) { 14: int sum = 0; 15: foreach (int i in nums) 16: sum += i;
17: return sum; 18: }
19:
20: int total = Sum(4, 3, 2, 1); // returns 10 21:
22: /* C# 4.0 supports optional parameters. Previous versions required function overloading. */ 23: void SayHello(string name, string prefix = "") { 24: Console.WriteLine("Greetings, " + prefix + " " + name); 25: }
26:
27: SayHello("Strangelove", "Dr."); 28: SayHello("Mom"); |
| Strings | |
1: 'Special character constants (all also accessible from ControlChars class) 2: vbCrLf, vbCr, vbLf, vbNewLine
3: vbNullString
4: vbTab
5: vbBack
6: vbFormFeed
7: vbVerticalTab
8: "" 9:
10: ' String concatenation (use & or +) 11: Dim school As String = "Harding" & vbTab 12: school = school & "University" ' school is "Harding (tab) University" 13: school &= "University" ' Same thing (+= does the same) 14:
15: ' Chars 16: Dim letter As Char = school.Chars(0) ' letter is H 17: letter = "Z"c ' letter is Z 18: letter = Convert.ToChar(65) ' letter is A 19: letter = Chr(65) ' same thing 20: Dim word() As Char = school.ToCharArray ' word holds Harding 21:
22: ' No string literal operator 23: Dim filename As String = "c:\temp\x.dat" 24:
25: ' String comparison 26: Dim mascot As String = "Bisons" 27: If (mascot = "Bisons") Then ' true 28: If (mascot.Equals("Bisons")) Then ' true 29: If (mascot.ToUpper().Equals("BISONS")) Then ' true 30: If (mascot.CompareTo("Bisons") = 0) Then ' true 31:
32: ' String matching with Like - Regex is more powerful 33: If ("John 3:16" Like "Jo[Hh]? #:*") Then 'true 34:
35: ' Substring 36: s = mascot.Substring(2, 3)) ' son 37: s = Mid("testing", 2, 3) ' est 38:
39: ' Replacement 40: s = mascot.Replace("sons", "nomial")) ' s is "Binomial" 41:
42: ' Split 43: Dim names As String = "Michael,Dwight,Jim,Pam" 44: Dim parts() As String = names.Split(",".ToCharArray()) ' One name in each slot 45:
46: ' Date to string 47: Dim dt As New DateTime(1973, 10, 12) 48: Dim s As String = "My birthday: " & dt.ToString("MMM dd, yyyy") ' Oct 12, 1973 49:
50: ' Integer to String 51: Dim x As Integer = 2 52: Dim y As String = x.ToString() ' y is "2" 53:
54: ' String to Integer 55: Dim x As Integer = Convert.ToInt32("-5") ' x is -5 56:
57: ' Mutable string 58: Dim buffer As New System.Text.StringBuilder("two ") 59: buffer.Append("three ") 60: buffer.Insert(0, "one ") 61: buffer.Replace("two", "TWO") 62: Console.WriteLine(buffer) ' Prints "one TWO three" |
1: //Escape sequences 2: \r // carriage-return 3: \n // line-feed 4: \t // tab 5: \\ // backslash 6: \" // quote" 7:
8:
9: // String concatenation 10: string school = "Harding\t"; 11: school = school + "University"; // school is "Harding (tab) University" 12: school += "University"; // Same thing 13:
14: // Chars 15: char letter = school[0]; // letter is H 16: letter = 'Z'; // letter is Z 17: letter = Convert.ToChar(65); // letter is A 18: letter = (char)65; // same thing 19: char[] word = school.ToCharArray(); // word holds Harding 20:
21: // String literal 22: string filename = @"c:\temp\x.dat"; // Same as "c:\\temp\\x.dat" 23:
24: // String comparison 25: string mascot = "Bisons"; 26: if (mascot == "Bisons") // true 27: if (mascot.Equals("Bisons")) // true 28: if (mascot.ToUpper().Equals("BISONS")) // true 29: if (mascot.CompareTo("Bisons") == 0) // true 30:
31: // String matching - No Like equivalent, use Regex 32:
33:
34: // Substring 35: s = mascot.Substring(2, 3)) // son 36: s = "testing".Substring(1, 3); // est (no Mid) 37:
38: // Replacement 39: s = mascot.Replace("sons", "nomial")) // Binomial 40:
41: // Split 42: string names = "Michael,Dwight,Jim,Pam"; 43: string[] parts = names.Split(",".ToCharArray()); // One name in each slot 44:
45: // Date to string 46: DateTime dt = new DateTime(1973, 10, 12); 47: string s = dt.ToString("MMM dd, yyyy"); // Oct 12, 1973 48:
49: // int to string 50: int x = 2; 51: string y = x.ToString(); // y is "2" 52: // string to int 53: int x = Convert.ToInt32("-5"); // x is -5 54:
55: // Mutable string 56: System.Text.StringBuilder buffer = new System.Text.StringBuilder("two "); 57: buffer.Append("three "); 58: buffer.Insert(0, "one "); 59: buffer.Replace("two", "TWO"); 60: Console.WriteLine(buffer); // Prints "one TWO three" |
| Regular Expressions | |
1: Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions 2:
3: ' Match a string pattern 4: Dim r As New Regex("j[aeiou]h?. \d:*", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase Or _ 5: RegexOptions.Compiled)
6: If (r.Match("John 3:16").Success) Then 'true 7: Console.WriteLine("Match") 8: End If 9:
10: ' Find and remember all matching patterns 11: Dim s As String = "My number is 305-1881, not 305-1818." 12: Dim r As New Regex("(\d+-\d+)") 13: Dim m As Match = r.Match(s) ' Matches 305-1881 and 305-1818 14: While m.Success 15: Console.WriteLine("Found number: " & m.Groups(1).Value & " at position " _ 16: & m.Groups(1).Index.ToString)
17: m = m.NextMatch()
18: End While 19:
20: ' Remeber multiple parts of matched pattern 21: Dim r As New Regex("(\d\d):(\d\d) (am|pm)") 22: Dim m As Match = r.Match("We left at 03:15 pm.") 23: If m.Success Then 24: Console.WriteLine("Hour: " & m.Groups(1).ToString) ' 03 25: Console.WriteLine("Min: " & m.Groups(2).ToString) ' 15 26: Console.WriteLine("Ending: " & m.Groups(3).ToString) ' pm 27: End If 28:
29: ' Replace all occurrances of a pattern 30: Dim r As New Regex("h\w+?d", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase) 31: Dim s As String = r.Replace("I heard this was HARD!", "easy") ' I easy this was easy! 32:
33: ' Replace matched patterns 34: Dim s As String = Regex.Replace("123 < 456", "(\d+) . (\d+)", "$2 > $1") ' 456 > 123 35:
36: ' Split a string based on a pattern 37: Dim names As String = "Michael, Dwight, Jim, Pam" 38: Dim r As New Regex(",\s*") 39: Dim parts() As String = r.Split(names) ' One name in each slot |
1: using System.Text.RegularExpressions; 2:
3: // Match a string pattern 4: Regex r = new Regex(@"j[aeiou]h?. \d:*", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase | 5: RegexOptions.Compiled);
6: if (r.Match("John 3:16").Success) // true 7: Console.WriteLine("Match"); 8:
9:
10: // Find and remember all matching patterns 11: string s = "My number is 305-1881, not 305-1818."; 12: Regex r = new Regex("(\\d+-\\d+)"); 13: // Matches 305-1881 and 305-1818 14: for (Match m = r.Match(s); m.Success; m = m.NextMatch()) 15: Console.WriteLine("Found number: " + m.Groups[1] + " at position " + 16: m.Groups[1].Index);
17:
18:
19:
20: // Remeber multiple parts of matched pattern 21: Regex r = new Regex("@(\d\d):(\d\d) (am|pm)"); 22: Match m = r.Match("We left at 03:15 pm."); 23: if (m.Success) { 24: Console.WriteLine("Hour: " + m.Groups[1]); // 03 25: Console.WriteLine("Min: " + m.Groups[2]); // 15 26: Console.WriteLine("Ending: " + m.Groups[3]); // pm 27: }
28:
29: // Replace all occurrances of a pattern 30: Regex r = new Regex("h\\w+?d", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase); 31: string s = r.Replace("I heard this was HARD!", "easy")); // I easy this was easy! 32:
33: // Replace matched patterns 34: string s = Regex.Replace("123 < 456", @"(\d+) . (\d+)", "$2 > $1"); // 456 > 123 35:
36: // Split a string based on a pattern 37: string names = "Michael, Dwight, Jim, Pam"; 38: Regex r = new Regex(@",\s*"); 39: string[] parts = r.Split(names); // One name in each slot |
| Exception Handling | |
1: ' Throw an exception 2: Dim ex As New Exception("Something is really wrong.") 3: Throw ex 4:
5: ' Catch an exception 6: Try 7: y = 0
8: x = 10 / y
9: Catch ex As Exception When y = 0 ' Argument and When is optional 10: Console.WriteLine(ex.Message)
11: Finally 12: Beep()
13: End Try 14:
15: ' Deprecated unstructured error handling 16: On Error GoTo MyErrorHandler 17: ...
18: MyErrorHandler: Console.WriteLine(Err.Description)
|
1: Exception up = new Exception("Something is really wrong."); 2: throw up; // ha ha 3:
4: // Catch an exception 5: try { 6: y = 0;
7: x = 10 / y;
8: }
9: catch (Exception ex) { // Argument is optional, no "When" keyword 10: Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
11: }
12: finally { 13: Microsoft.VisualBasic.Interaction.Beep();
14: }
|
| Namespaces | |
1: Namespace Harding.Compsci.Graphics 2: ...
3: End Namespace 4:
5: ' or 6:
7: Namespace Harding 8: Namespace Compsci 9: Namespace Graphics 10: ...
11: End Namespace 12: End Namespace 13: End Namespace 14:
15: Imports Harding.Compsci.Graphics |
1: namespace Harding.Compsci.Graphics { 2: ...
3: }
4:
5: // or 6:
7: namespace Harding { 8: namespace Compsci { 9: namespace Graphics { 10: ...
11: }
12: }
13: }
14:
15: using Harding.Compsci.Graphics; |
| Attributes | |
1: ' Attribute can be applied to anything 2: Public Class IsTestedAttribute 3: Inherits Attribute 4: End Class 5:
6: ' Attribute can only be applied to classes or structs 7: <AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class Or AttributeTargets.Struct)> 8: Public Class AuthorAttribute 9: Inherits Attribute 10:
11: Public Property Name As String 12: Public Property Version As Integer = 0 13:
14: Public Sub New(ByVal name As String) 15: Me.Name = name 16: End Sub 17: End Class 18:
19: <Author("Sue", Version:=3)> 20: Class Shape 21:
22: <IsTested()>
23: Sub Move() 24: ' Do something... 25: End Sub 26: End Class |
1: // Attribute can be applied to anything 2: public class IsTestedAttribute : Attribute 3: {
4: }
5:
6: // Attribute can only be applied to classes or structs 7: [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Struct)]
8: public class AuthorAttribute : Attribute { 9:
10: public string Name { get; set; } 11: public int Version { get; set; } 12:
13: public AuthorAttribute(string name) { 14: Name = name;
15: Version = 0;
16: }
17: }
18:
19: [Author("Sue", Version = 3)] 20: class Shape { 21:
22: [IsTested]
23: void Move() { 24: // Do something... 25: }
26: }
|
| Classes & Interfaces | |
1: 'Access Modifiers 2: Public 3: Private 4: Friend 5: Protected 6: Protected Friend 7:
8: 'Class Modifiers 9: MustInherit 10: NotInheritable 11:
12: 'Method Modifiers 13: MustOverride 14: NotInheritable 15: Shared 16: Overridable 17:
18: ' All members are Shared 19: Module 20:
21: ' Partial classes 22: Partial Class Team 23: ...
24: Protected name As String 25: Public Overridable Sub DisplayName() 26: Console.WriteLine(name)
27: End Sub 28: End Class 29:
30: ' Inheritance 31: Class FootballTeam 32: Inherits Team 33: ...
34: Public Overrides Sub DisplayName() 35: Console.WriteLine("** " + name + " **") 36: End Sub 37: End Class 38:
39: ' Interface definition 40: Interface IAlarmClock 41: Sub Ring() 42: Property TriggerDateTime() As DateTime 43: End Interface 44:
45: ' Extending an interface 46: Interface IAlarmClock 47: Inherits IClock 48: ...
49: End Interface 50:
51: ' Interface implementation 52: Class WristWatch 53: Implements IAlarmClock, ITimer 54:
55: Public Sub Ring() Implements IAlarmClock.Ring 56: Console.WriteLine("Wake up!") 57: End Sub 58:
59: Public Property TriggerDateTime As DateTime Implements IAlarmClock.TriggerDateTime 60: ...
61: End Class |
1: //Access Modifiers 2: public 3: private 4: internal 5: protected 6: protected internal 7:
8: //Class Modifiers 9: abstract 10: sealed 11: static 12:
13: //Method Modifiers 14: abstract 15: sealed 16: static 17: virtual 18:
19: //No Module equivalent - just use static class 20:
21: // Partial classes 22: partial class Team { 23: ...
24: protected string name; 25: public virtual void DislpayName() { 26: Console.WriteLine(name);
27: }
28:
29:
30: // Inheritance 31: class FootballTeam : Team { 32: ...
33: public override void DislpayName() { 34: Console.WriteLine("** " + name + " **"); 35: }
36: }
37:
38:
39: // Interface definition 40: interface IAlarmClock { 41: void Ring(); 42: DateTime CurrentDateTime { get; set; } 43: }
44:
45: // Extending an interface 46: interface IAlarmClock : IClock { 47: ...
48: }
49:
50:
51: // Interface implementation 52: class WristWatch : IAlarmClock, ITimer { 53:
54: public void Ring() { 55: Console.WriteLine("Wake up!"); 56: }
57:
58: public DateTime TriggerDateTime { get; set; } 59: ...
60: }
|
| Constructors & Destructors | |
1: Class SuperHero 2: Inherits Person 3:
4: Private powerLevel As Integer 5: Private name As String 6:
7: ' Default constructor 8: Public Sub New() 9: powerLevel = 0
10: name = "Super Bison" 11: End Sub 12:
13: Public Sub New(ByVal powerLevel As Integer) 14: Me.New("Super Bison") ' Call other constructor 15: Me.powerLevel = powerLevel 16: End Sub 17:
18: Public Sub New(ByVal name As String) 19: MyBase.New(name) ' Call base classes' constructor 20: Me.name = name 21: End Sub 22:
23: Shared Sub New() 24: ' Shared constructor invoked before 1st instance is created 25: End Sub 26:
27: Protected Overrides Sub Finalize() 28: ' Destructor to free unmanaged resources 29: MyBase.Finalize() 30: End Sub 31: End Class |
1: class SuperHero : Person { 2:
3: private int powerLevel; 4: private string name; 5:
6:
7: // Default constructor 8: public SuperHero() { 9: powerLevel = 0;
10: name = "Super Bison"; 11: }
12:
13: public SuperHero(int powerLevel) 14: : this("Super Bison") { // Call other constructor 15: this.powerLevel = powerLevel; 16: }
17:
18: public SuperHero(string name) 19: : base(name) { // Call base classes' constructor 20: this.name = name; 21: }
22:
23: static SuperHero() { 24: // Static constructor invoked before 1st instance is created 25: }
26:
27: ~SuperHero() {
28: // Destructor implicitly creates a Finalize method 29: }
30:
31: }
|
| Using Objects | |
1: Dim hero As SuperHero = New SuperHero 2: ' or 3: Dim hero As New SuperHero 4:
5: With hero 6: .Name = "SpamMan" 7: .PowerLevel = 3
8: End With 9:
10: hero.Defend("Laura Jones") 11: hero.Rest() ' Calling Shared method 12: ' or 13: SuperHero.Rest()
14:
15: Dim hero2 As SuperHero = hero ' Both reference the same object 16: hero2.Name = "WormWoman" 17: Console.WriteLine(hero.Name) ' Prints WormWoman 18:
19: hero = Nothing ' Free the object 20:
21: If hero Is Nothing Then _ 22: hero = New SuperHero 23:
24: Dim obj As Object = New SuperHero 25: If TypeOf obj Is SuperHero Then _ 26: Console.WriteLine("Is a SuperHero object.") 27:
28: ' Mark object for quick disposal 29: Using reader As StreamReader = File.OpenText("test.txt") 30: Dim line As String = reader.ReadLine() 31: While Not line Is Nothing 32: Console.WriteLine(line)
33: line = reader.ReadLine()
34: End While 35: End Using |
1: SuperHero hero = new SuperHero(); 2:
3:
4:
5: // No "With" but can use object initializers 6: SuperHero hero = new SuperHero() { Name = "SpamMan", PowerLevel = 3 }; 7:
8: hero.Defend("Laura Jones"); 9: SuperHero.Rest(); // Calling static method 10:
11:
12:
13: SuperHero hero2 = hero; // Both reference the same object 14: hero2.Name = "WormWoman"; 15: Console.WriteLine(hero.Name); // Prints WormWoman 16:
17: hero = null ; // Free the object 18:
19: if (hero == null) 20: hero = new SuperHero(); 21:
22: Object obj = new SuperHero(); 23: if (obj is SuperHero) 24: Console.WriteLine("Is a SuperHero object."); 25: // Mark object for quick disposal 26: using (StreamReader reader = File.OpenText("test.txt")) { 27: string line; 28: while ((line = reader.ReadLine()) != null) 29: Console.WriteLine(line);
30: }
|
| Structs | |
1: Structure Student 2: Public name As String 3: Public gpa As Single 4:
5: Public Sub New(ByVal name As String, ByVal gpa As Single) 6: Me.name = name 7: Me.gpa = gpa 8: End Sub 9: End Structure 10:
11: Dim stu As Student = New Student("Bob", 3.5) 12: Dim stu2 As Student = stu 13:
14: stu2.name = "Sue" 15: Console.WriteLine(stu.name) ' Prints Bob 16: Console.WriteLine(stu2.name) ' Prints Sue
|
1: struct Student { 2: public string name; 3: public float gpa; 4:
5: public Student(string name, float gpa) { 6: this.name = name; 7: this.gpa = gpa; 8: }
9: }
10:
11: Student stu = new Student("Bob", 3.5f); 12: Student stu2 = stu;
13:
14: stu2.name = "Sue"; 15: Console.WriteLine(stu.name); // Prints Bob 16: Console.WriteLine(stu2.name); // Prints Sue |
| Properties | |
1: ' Auto-implemented properties are new to VB10 2: Public Property Name As String 3: Public Property Size As Integer = -1 ' Default value, Get and Set both Public 4:
5: ' Traditional property implementation 6: Private mName As String 7: Public Property Name() As String 8: Get 9: Return mName 10: End Get 11: Set(ByVal value As String) 12: mName = value
13: End Set 14: End Property 15:
16: ' Read-only property 17: Private mPowerLevel As Integer 18: Public ReadOnly Property PowerLevel() As Integer 19: Get 20: Return mPowerLevel 21: End Get 22: End Property 23:
24: ' Write-only property 25: Private mHeight As Double 26: Public WriteOnly Property Height() As Double 27: Set(ByVal value As Double) 28: mHeight = If(value < 0, mHeight = 0, mHeight = value) 29: End Set 30: End Property |
1: // Auto-implemented properties 2: public string Name { get; set; } 3: public int Size { get; protected set; } // Set default value in constructor 4:
5: // Traditional property implementation 6: private string name; 7: public string Name { 8: get { 9: return name; 10: }
11: set { 12: name = value;
13: }
14: }
15:
16: // Read-only property 17: private int powerLevel; 18: public int PowerLevel { 19: get { 20: return powerLevel; 21: }
22: }
23:
24: // Write-only property 25: private double height; 26: public double Height { 27: set { 28: height = value < 0 ? 0 : value;
29: }
30: }
|
| Generics | |
1: ' Enforce accepted data type at compile-time 2: Dim numbers As New List(Of Integer) 3: numbers.Add(2)
4: numbers.Add(4)
5: DisplayList(Of Integer)(numbers) 6:
7: ' Subroutine can display any type of List 8: Sub DisplayList(Of T)(ByVal list As List(Of T)) 9: For Each item As T In list 10: Console.WriteLine(item)
11: Next 12: End Sub 13:
14: ' Class works on any data type 15: Class SillyList(Of T) 16: Private list(10) As T 17: Private rand As New Random 18:
19: Public Sub Add(ByVal item As T) 20: list(rand.Next(10)) = item 21: End Sub 22:
23: Public Function GetItem() As T 24: Return list(rand.Next(10)) 25: End Function 26: End Class 27:
28: ' Limit T to only types that implement IComparable 29: Function Maximum(Of T As IComparable)(ByVal ParamArray items As T()) As T 30: Dim max As T = items(0) 31: For Each item As T In items 32: If item.CompareTo(max) > 0 Then max = item 33: Next 34: Return max 35: End Function |
1: // Enforce accepted data type at compile-time 2: List<int> numbers = new List<int>(); 3: numbers.Add(2);
4: numbers.Add(4);
5: DisplayList<int>(numbers); 6:
7: // Function can display any type of List 8: void DisplayList<T>(List<T> list) { 9: foreach (T item in list) 10: Console.WriteLine(item);
11: }
12:
13: // Class works on any data type 14: class SillyList<T> { 15: private T[] list = new T[10]; 16: private Random rand = new Random(); 17:
18: public void Add(T item) { 19: list[rand.Next(10)] = item;
20: }
21:
22: public T GetItem() { 23: return list[rand.Next(10)]; 24: }
25: }
26:
27: // Limit T to only types that implement IComparable 28: T Maximum<T>(params T[] items) where T : IComparable<T> { 29: T max = items[0];
30: foreach (T item in items) 31: if (item.CompareTo(max) > 0) 32: max = item;
33: return max; 34: }
|
| Events | |
1: Delegate Sub MsgArrivedEventHandler(ByVal message As String) 2:
3: Event MsgArrivedEvent As MsgArrivedEventHandler 4:
5: ' or to define an event which declares a delegate implicitly 6: Event MsgArrivedEvent(ByVal message As String) 7:
8: AddHandler MsgArrivedEvent, AddressOf My_MsgArrivedCallback 9: ' Won't throw an exception if obj is Nothing 10: RaiseEvent MsgArrivedEvent("Test message") 11: RemoveHandler MsgArrivedEvent, AddressOf My_MsgArrivedCallback 12:
13: Imports System.Windows.Forms 14:
15: Dim WithEvents MyButton As Button ' WithEvents can't be used on local variable 16: MyButton = New Button 17:
18: Sub MyButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ 19: ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyButton.Click 20: MessageBox.Show(Me, "Button was clicked", "Info", _ 21: MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information)
22: End Sub |
1: delegate void MsgArrivedEventHandler(string message); 2:
3: event MsgArrivedEventHandler MsgArrivedEvent; 4:
5: // Delegates must be used with events in C# 6:
7:
8: MsgArrivedEvent += new MsgArrivedEventHandler(My_MsgArrivedEventCallback); 9: MsgArrivedEvent("Test message"); // Throws exception if obj is null 10: MsgArrivedEvent -= new MsgArrivedEventHandler(My_MsgArrivedEventCallback); 11:
12:
13:
14: using System.Windows.Forms; 15:
16: Button MyButton = new Button(); 17: MyButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(MyButton_Click); 18:
19: void MyButton_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { 20: MessageBox.Show(this, "Button was clicked", "Info", 21: MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
22: }
|
| Delegates & Lambda Expressions | |
1: Delegate Sub HelloDelegate(ByVal s As String) 2:
3: Sub SayHello(ByVal s As String) 4: Console.WriteLine("Hello, " & s) 5: End Sub 6: ' Create delegate that calls SayHello 7: Dim hello As HelloDelegate = AddressOf SayHello 8: hello("World") ' Or hello.Invoke("World") 9:
10: ' Use lambda expression (anonymous method) instead of a delegate 11: Dim hello2 = Sub(x) Console.WriteLine("Hello, " & x) 12: hello2("World") 13:
14:
15:
16:
17:
18:
19: ' Use Func(Of T, TResult) delegate to call Uppercase 20: Dim convert As Func(Of String, String) = AddressOf Uppercase 21: Console.WriteLine(convert("test")) 22:
23: Function Uppercase(s As String) As String 24: Return s.ToUpper 25: End Function 26:
27: ' Declare and invoke lambda expression 28: Console.WriteLine((Function(num As Integer) num + 1)(2)) 29:
30: ' Pass lambda expression as an argument 31: TestValues(Function(x, y) x Mod y = 0) 32:
33: Sub TestValues(ByVal f As Func(Of Integer, Integer, Boolean)) 34: If f(8, 4) Then 35: Console.WriteLine("true") 36: Else 37: Console.WriteLine("false") 38: End If 39: End Sub |
1: delegate void HelloDelegate(string s); 2:
3: void SayHello(string s) { 4: Console.WriteLine("Hello, " + s); 5: }
6:
7: // C# 1.0 delegate syntax with named method 8: HelloDelegate hello = new HelloDelegate(SayHello); 9: hello("World"); // Or hello.Invoke("World"); 10:
11: // C# 2.0 delegate syntax with anonymous method 12: HelloDelegate hello2 = delegate(string s) { 13: Console.WriteLine("Hello, " + s); 14: };
15: hello2("World"); 16:
17: // C# 3.0 delegate syntax with lambda expression 18: HelloDelegate hello3 = s => { Console.WriteLine("Hello, " + s); }; 19: hello3("World"); 20:
21: // Use Func<in T, out TResult> delegate to call Uppercase 22: Func<string, string> convert = Uppercase; 23: Console.WriteLine(convert("test")); 24:
25: string Uppercase(string s) { 26: return s.ToUpper(); 27: }
28:
29: // Declare and invoke Func using a lambda expression 30: Console.WriteLine(new Func<int, int>(num => num + 1)(2)); 31:
32: // Pass lamba expression as an argument 33: TestValues((x, y) => x % y == 0);
34:
35: void TestValues(Func<int, int, bool> f) { 36: if (f(8, 4)) 37: Console.WriteLine("true"); 38: else 39: Console.WriteLine("false"); 40: }
|
| Extension Methods | |
1: Imports System.Runtime.CompilerServices 2:
3: Module StringExtensions 4: <Extension()>
5: Public Function VowelCount(ByVal s As String) As Integer 6: Return s.Count(Function(c) "aeiou".Contains(Char.ToLower(c))) 7: End Function 8: End Module 9:
10: ' Using the extension method 11: Console.WriteLine("This is a test".VowelCount) |
1: public static class StringExtensions { 2: public static int VowelCount(this string s) { 3: return s.Count(c => "aeiou".Contains(Char.ToLower(c))); 4: }
5: }
6:
7:
8:
9: // Using the extension method 10: Console.WriteLine("This is a test".VowelCount()); |
| LINQ | |
1: Dim nums() As Integer = {5, 8, 2, 1, 6} 2:
3: ' Get all numbers in the array above 4 4: Dim results = From n In nums 5: Where n > 4
6: Select n 7:
8: ' Same thing using lamba expression 9: results = nums.Where(Function(n) n > 4) 10:
11: ' Displays 5 8 6 12: For Each n As Integer In results 13: Console.Write(n & " ") 14: Next 15:
16: Console.WriteLine(results.Count()) ' 3 17: Console.WriteLine(results.First()) ' 5 18: Console.WriteLine(results.Last()) ' 6 19: Console.WriteLine(results.Average()) ' 6.33333 20:
21: results = results.Intersect({5, 6, 7}) ' 5 6 22: results = results.Concat({5, 1, 5}) ' 5 6 5 1 5 23: results = results.Distinct() ' 5 6 1 24:
25: Dim Students() As Student = { 26: New Student With {.Name = "Bob", .Gpa = 3.5}, 27: New Student With {.Name = "Sue", .Gpa = 4.0}, 28: New Student With {.Name = "Joe", .Gpa = 1.9} 29: }
30:
31: ' Get a list of students ordered by Gpa with Gpa >= 3.0 32: Dim goodStudents = From s In Students 33: Where s.Gpa >= 3.0
34: Order By s.Gpa Descending
35: Select s 36:
37: Console.WriteLine(goodStudents.First.Name) ' Sue
|
1: int[] nums = { 5, 8, 2, 1, 6 }; 2:
3: // Get all numbers in the array above 4 4: var results = from n in nums 5: where n > 4
6: select n;
7:
8: // Same thing using lamba expression 9: results = nums.Where(n => n > 4);
10:
11: // Displays 5 8 6 12: foreach (int n in results) 13: Console.Write(n + " "); 14:
15:
16: Console.WriteLine(results.Count()); // 3 17: Console.WriteLine(results.First()); // 5 18: Console.WriteLine(results.Last()); // 6 19: Console.WriteLine(results.Average()); // 6.33333 20:
21: results = results.Intersect(new[] {5, 6, 7}); // 5 6 22: results = results.Concat(new[] {5, 1, 5}); // 5 6 5 1 5 23: results = results.Distinct(); // 5 6 1 24:
25: Student[] Students = {
26: new Student{ Name = "Bob", Gpa = 3.5 }, 27: new Student{ Name = "Sue", Gpa = 4.0 }, 28: new Student{ Name = "Joe", Gpa = 1.9 } 29: };
30:
31: // Get a list of students ordered by Gpa with Gpa >= 3.0 32: var goodStudents = from s in Students 33: where s.Gpa >= 3.0
34: orderby s.Gpa descending
35: select s;
36:
37: Console.WriteLine(goodStudents.First().Name); // Sue |
| Razor syntax (Special ASP.NET tags) | |
1: 'Implicit expression 2: @name Hello, <b>@name.</b> 3:
4: 'Explicit expression 5: @(5+5) Hello, @name. Your age is: <b>@(5+5).</b> 6:
7: 'Unencoded expression 8: @Html.Raw(name) Hello, <b>@Html.Raw(name).</b> 9:
10: 'Multi-statement code blocks 11: @Code 12: /* VB.NET Code goes here */
13: End Code 14: @Code 15: Dim greeting = "Hello, world!" 16: For i = 1 To 3 17: @<p>@greeting (@i)</p> 18: Next i 19: End Code 20:
21: 'Plain text inside a code block 22: @Code 23: @:Plain text goes here 24: End Code 25: @If IsPost Then 26: Dim text = "Code goes here..." 27: @:Plain text goes here... 28: End If 29:
30: 'Plain text inside a code block (alternative) 31: @<text>Plain text goes here...</text> 32: @If IsPost Then 33: Dim text = "Code goes here..." 34: @<text>Plain text goes here...</text> 35: End If 36:
37: 'Server-side comment 38: @* 39: Here's a Razor server-side comment
40: It won't be rendered to the browser
41: It can span multiple lines
42: *@ 43:
44: 'Conditional attribute (New in MVC 4) 45: <div style="@divStyle">Hello, world!</div> 46: @Code 47: Dim divStyle As String 48: If Request.QueryString("style") IsNot Nothing Then 49: divStyle = "background-color: yellow;" 50: End If 51: End Code 52: <div style="@divStyle">Hello, world!</div> |
1: //Implicit expression 2: @name Hello, <b>@name.</b> 3:
4: //Explicit expression 5: @(5+5) Hello, @name. Your age is: <b>@(5+5).</b> 6:
7: //Unencoded expression 8: @Html.Raw(name) Hello, <b>@Html.Raw(name).</b> 9:
10: //Multi-statement code blocks 11: @{ 12: /* C# Code goes here */ 13: }
14: @{ 15: var greeting = "Hello, world!"; 16: for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) 17: {
18: <p>@greeting (@i)</p> 19: }
20: }
21:
22: //Plain text inside a code block 23: @:Plain text goes here... 24: @if(isTrue) 25: {
26: var text = "Code goes here..."; 27: @:Plain text goes here... 28: }
29:
30: //Plain text inside a code block (alternative) 31: <text>Plain text goes here...</text>
32: @if(isTrue) 33: {
34: var text = "Code goes here..."; 35: <text>Plain text goes here...</text>
36: }
37:
38: //Server-side comment 39: @* 40: Here's a Razor server-side comment
41: It won't be rendered to the browser
42: It can span multiple lines
43: *@ 44:
45: //Conditional attribute (New in MVC 4) 46: <div style="@divStyle">Hello, world!</div> 47: @{ 48: string divStyle = null; 49: if(Request.QueryString["style"] != null) 50: {
51: divStyle = "background-color: yellow;"; 52: }
53: }
54: <div style="@divStyle">Hello, world!</div> |
Microsoft context:
 )
)
|
|